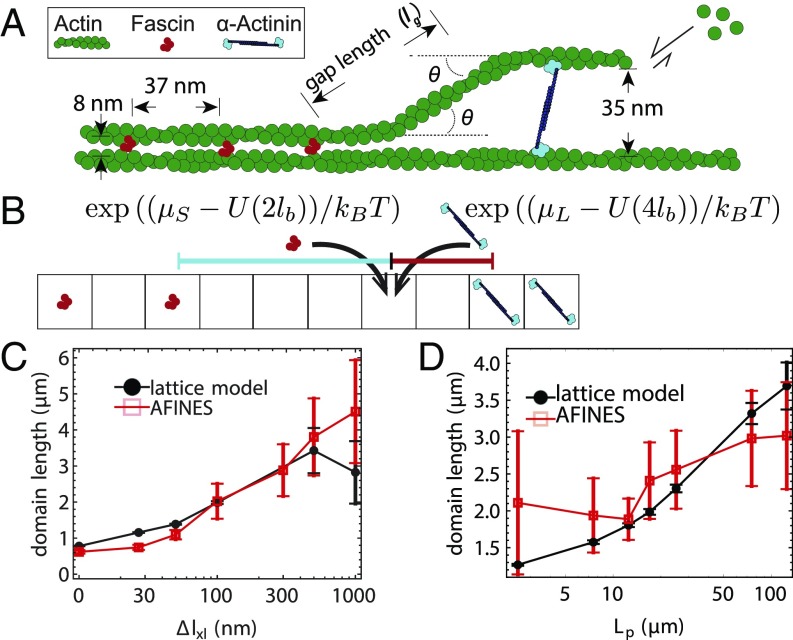
Fig. 2.
Effect of cross-linker and filament mechanics on domain length. (A) Schematic of a 2-filament bundle transitioning from a tight fascin bundle to a wider-spaced -actinin bundle in an idealized geometry. The filament bends twice at an angle , leaving a gap of length , defined along the contour of actin rather than between cross-linker centers so that the bending energy in the lattice model and AFINES have the same functional form. (B) Lattice model example, in which there is initially a gap of length indicated by the black dashed line and the indicated lattice site is empty. If that lattice site switches to a short cross-linker, the gap will reduce to (red solid line), whereas if it switches to a long cross-linker, the gap will reduce to (cyan solid line), yielding energy changes (). (C) Domain lengths from AFINES and lattice model as a function of cross-linker length difference (), with m, nm, and varying. (D) Same as C, but varying filament persistence length () while nm. In C and D, domain lengths are averaged over the last 100 s of a 2,000-s simulation, and 40 simulations; error bars are SEM. In D, filament repulsion ( pN) is also used to prohibit filaments from crossing each other, which occurred at low .