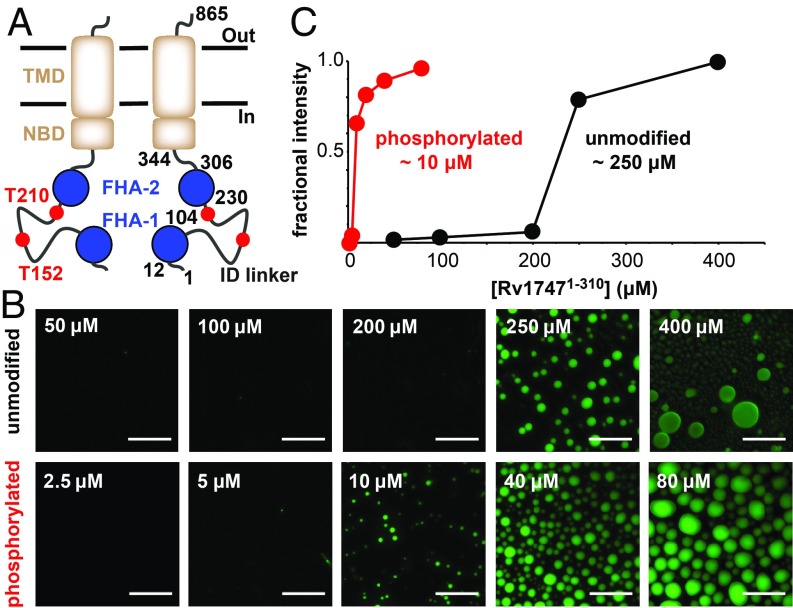
Fig. 1.
Rv17471–310 undergoes phosphorylation-enhanced phase separation into liquid-like droplets in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of Rv1747 as a homodimer with the regulatory module (FHA domains, blue; reported PknF phospho-acceptor sites T152/T210 in the ID linker, red) appended to the core ABC transporter (transmembrane domain [TMD] and nucleotide binding domain [NBD], brown, with boundaries indicated). (B) Unmodified and phosphorylated Rv17471–310 phase-separated at different threshold concentrations. Shown are fluorescent images of unmodified (Top) and phosphorylated (Bottom) OG-Rv17471–310, taken at 120 min after removal from the concentration device or after the addition of 0.5 μM PknF and 100 μM ATP, respectively. (Scale bars: 40 μm.) (C) The indicated saturation concentrations for phase separation were quantified by fractional fluorescence intensity.