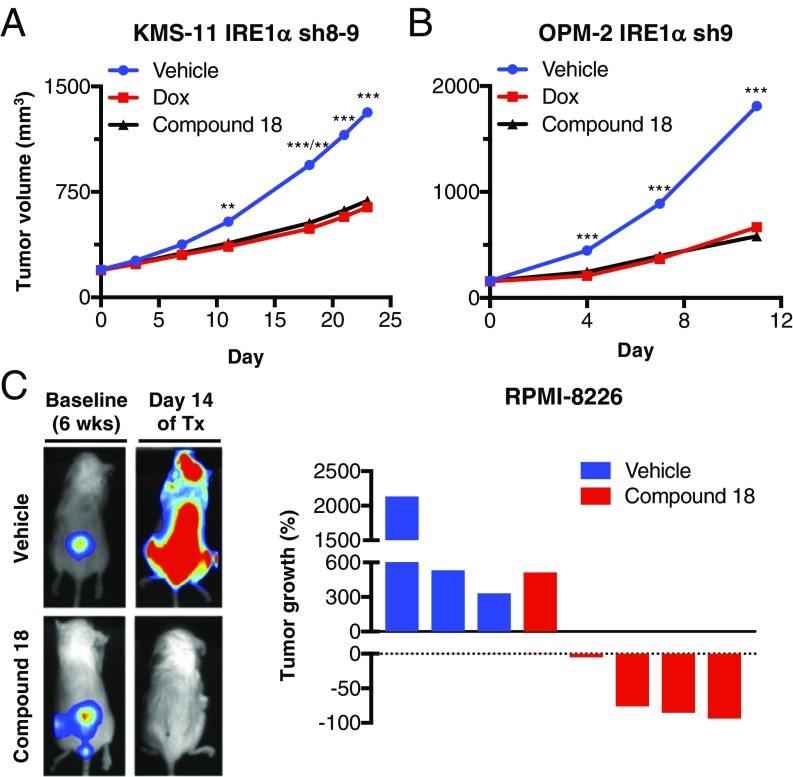
Fig. 4.
Small-molecule inhibition of IRE1α kinase attenuates s.c. and orthometastatic growth of human MM xenografts in mice. (A) KMS-11 cells stably transfected with doxycycline (Dox)-inducible shRNAs against IRE1α were inoculated s.c. into C.B-17 SCID mice and allowed to establish tumors of ∼200 mm3. Mice were then randomized into the following groups (n = 15 per group): vehicle, Dox in the drinking water (0.5 mg/kg), or compound 18 (30 mg/kg) intraperitoneally (IP) twice per day (BID). Tumor growth was monitored over 24 d. Individual tumor data are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S4C. (B) OPM-2 cells stably transfected with Dox-inducible shRNAs against IRE1α were inoculated s.c. into C.B-17 SCID mice and allowed to establish tumors of ∼160 mm3. Mice were then randomized (n = 14 per group) treated as in A with either vehicle, Dox in the drinking water, or compound 18 IP once per day and monitored for tumor growth over 11 d. Individual tumor data are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S4E. (C) RPMI-8226 cells expressing plasmids encoding mCherry and luciferase were injected i.v. via the tail vein of nonirradiated NOD/SCID/IL2rγ−/− mice and tumors were allowed to establish in the bone marrow over a period of 6 wk. Tumor burden was monitored by in-life imaging of luminescence. After 6 wk, mice were grouped out based on similar tumor burden, treated with vehicle (n = 3) or compound 18 (30 mg/kg IP, BID, n = 5) for 2 wk, and analyzed for tumor burden. One control mouse died during anesthesia and one treated mouse was killed due to weight loss. Luminescence images of representative mice are depicted on the left. The tumor burden of each mouse is shown as percent tumor growth on day 14 (at the end of 8 wk) compared with day 0 of treatment (Tx, at the end of 6 wk). **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.