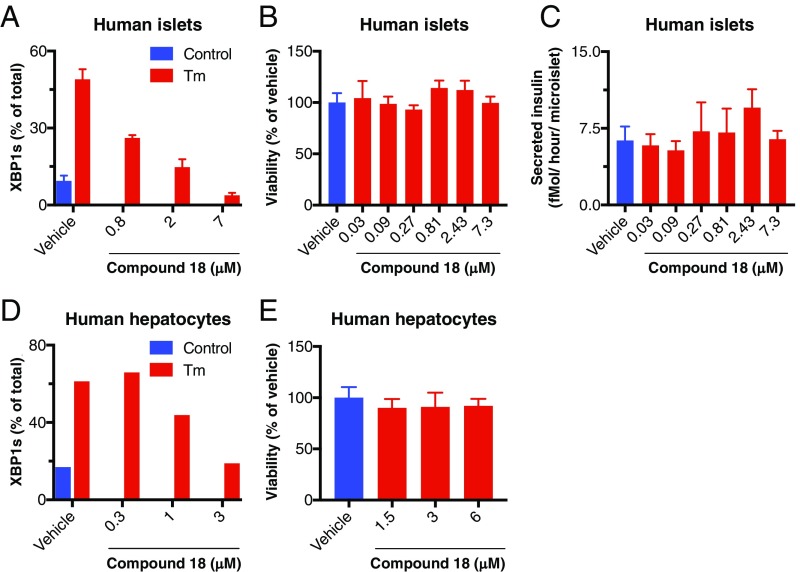
Fig. 6.
IRE1α kinase inhibition preserves survival and insulin secretion by pancreatic islet 3D microtissues and viability of primary hepatocytes. (A–C) Human pancreatic islets were isolated, dissociated, replated in microtiter wells (1,000 cells per drop), and allowed to form 3D microtissues over 7 d. Microtissues (n = 5 per treatment) were then (A) treated for 24 h with either vehicle control (DMSO) or tunicamycin (Tm, 5 μg/mL) in addition to either vehicle (DMSO) or compound 18, lysed, and then analyzed for XBP1s mRNA levels by RT-qPCR (%XBP1s mRNA is the ratio of XBP1s mRNA/(XBP1s mRNA+XBP1u mRNA); or (B and C) incubated for 7 d in the presence of either vehicle (DMSO) or compound 18 and then (B) analyzed for cell viability by CellTiter-Glo; or (C) challenged with glucose (16.7 mM) for 1 h and analyzed for insulin secretion by ELISA. (D and E) Human primary hepatocytes were treated for 8 h with either control or Tm in addition to either vehicle or compound 18 and analyzed for XBP1s levels as above by RT-qPCR (D). Alternatively, hepatocytes were cultured for 48 h in the presence of vehicle (DMSO) or compound 18 and analyzed for cell viability by CellTiter-Glo (E).