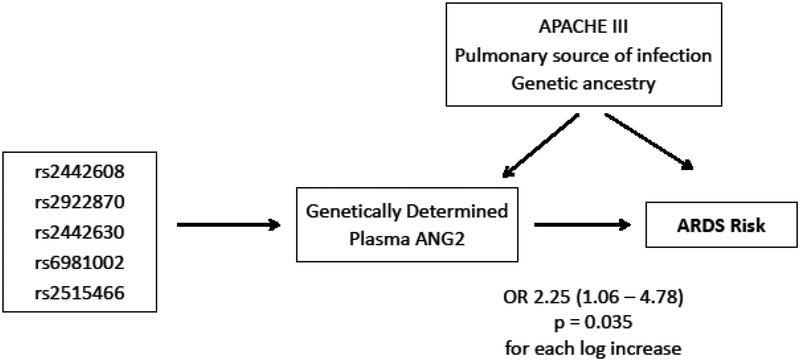
Figure 2: Mendelian Randomization conceptual model to infer whether plasma ANG2 has a causal effect on ARDS risk.
We first used linear regression to identify 5 SNPs near ANGPT2 that strongly associated with plasma ANG2 and jointly explained 8% of the variance in measured ANG2 among EA subjects. Each EA individual was then assigned a genetically predicted ANG2 value using post-estimation prediction. The predicted values should be less affected by unmeasured confounders beyond population stratification, since they derive from each individual’s genetic assortment of parental alleles. Genetically predicted plasma ANG2 values are then tested for an association with ARDS risk by multivariable logistic regression adjusting for genetic ancestry, severity of illness (APACHE III score), and pulmonary versus non-pulmonary source of sepsis. The statistically significant association between the genetically-determined component of plasma ANG2 and ARDS risk is evidence for a potential causal effect of plasma ANG2 towards ARDS development. SNPs: single nucleotide polymorphisms; ANGPT2: angiopoietin-2 gene; ANG2: angiopoietin-2 protein; EA: European ancestry.