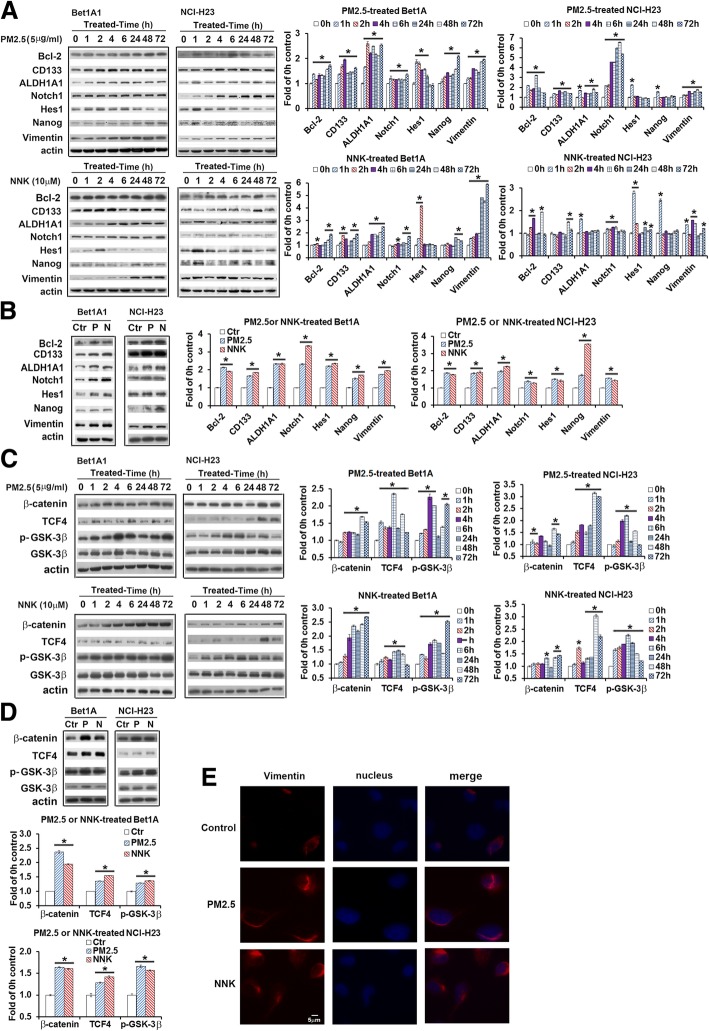
Fig. 2.
Effects of PM2.5 on oncogenic protein expression in Bet1A1 and NCI-H23 cells. a and (b) Effects of PM2.5 or NNK on lung carcinogenesis-related biomarkers; or (c) and (d) NNK or PM2.5 stimulated Wnt/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Cells were treated by 5 μg/ml PM2.5 or 10 μM NNK for 0 h, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h respectively (a and c). Cells of 0 h were the control condition. Or cells were treated with 5 μg/ml PM2.5 or 10 μM NNK for 28 days (b and d). Non-treated cells were cultured for 28 days as the control condition. Bcl-2, CD133, ALDH1A1, Notch1, Hes1, Nanog, vimentin, pGSK3β, GSK3β, β-catenin and TCF4 were detected by western blot. The quantification of protein was carried out by densitometry analysis and expressed as mean ± SE. The relative intensity of protein bands was summarized by column figure (n = 3, Ctr: non-treatment control; P: PM2.5; N: NNK; *p < 0.05 when compared each PM2.5- or NNK-treated condition with the control condition). e PM2.5 and NNK treatment increased vimentin expression. Bet1A Cells were treated with PM2.5 or NNK for 28 days. Vimentin antibody was used in connection with Rhodamine red-conjugated second antibody. DAPI (blue signal) was used for the counterstaining of the nucleus. The images were photographed (original magnification 400×, scale bar, 5 μm)