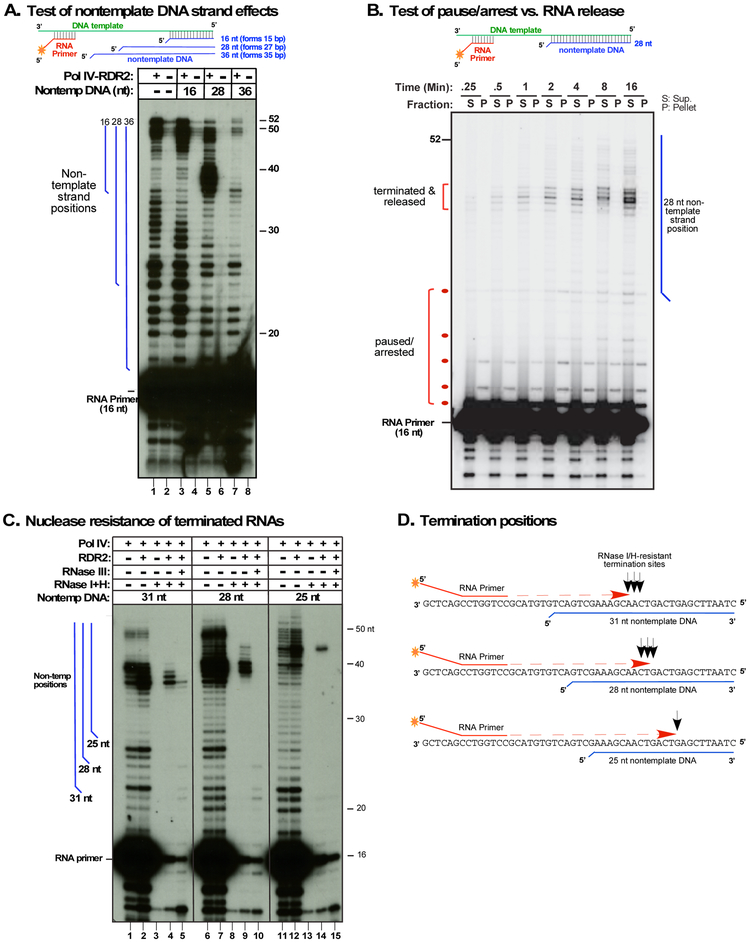
Figure 2. Nontemplate DNA induces Pol IV termination and dsRNA synthesis.
A. Test of non-template DNA strand effects on Pol IV transcription. Primer-initiated transcription was conducted as in Figure 1C but with nontemplate DNA strands of 16, 28 or 36 nt annealed to the template DNA (see also Figure S1B). Nontemplate DNA strands have an unpaired nucleotide at their 5' ends. Lanes 1, 3, 5, and 7 show reaction products of Pol IV-RDR2 complexes purified by virtue of the FLAG-tag on NRPD1. Lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8 are controls using non-transgenic plant extracts subjected to anti-FLAG affinity purification. Blue vertical lines to the left of the autoradiogram depict the positions of nontemplate strands relative to the transcripts.
B. Pol IV termination is induced by nontemplate DNA. Primer initiated transcription, using the template - 28 nt nontemplate strand pair, was conducted using Pol IV-RDR2 complexes immobilized on anti-FLAG resin. At the indicated timepoints, transcription reactions were subjected to centrifugation and RNAs of supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions subjected to denaturing PAGE and autoradiography.
C. Nontemplate DNA affects termination position and induces production of RNAs with the nuclease sensitivities of dsRNA. Pol IV affinity purified from RDR2 wild-type (+) or rdr2 mutant (−) backgrounds was tested for primer-initiated transcription of the DNA template annealed to 31nt, 28nt or 25nt nontemplate DNAs. Transcription products were incubated with RNAses I and H or RNase III, as indicated. Blue vertical lines represent positions of nontemplate strands.
D. Pol IV termination positions are not sequence-specific. The cartoon shows the positions (black arrows) of 3' ends of RNase I/H-resistant Pol IV transcripts relative to DNA template, RNA primer, and nontemplate DNA strands.