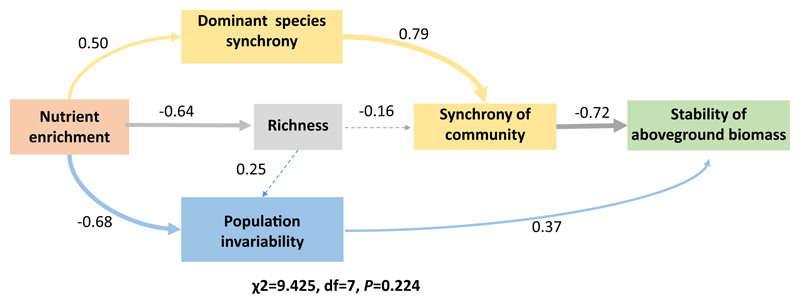
Fig. 6.
Structural equation model analysis of the contributions of species synchrony (paths colored yellow) and selection effect (paths colored blue) driven by nutrient enrichment to stability of aboveground biomass. Synchrony of dominant species contributed significantly to species synchrony of community which further contributed to ecosystem stability. Nutrient enrichment drove selection on more or less stable population which further contributed significantly to ecosystem stability. Nutrient enrichment-induced changes in species richness indirectly influence ecosystem stability via association with species synchrony and population invariability. The thicknesses of the arrows indicate the relative contributions of the variables. χ2, df, and P of the model fit are given. Values alongside arrow lines are standardized regression coefficients, indicating the contribution of each variable to the response. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)