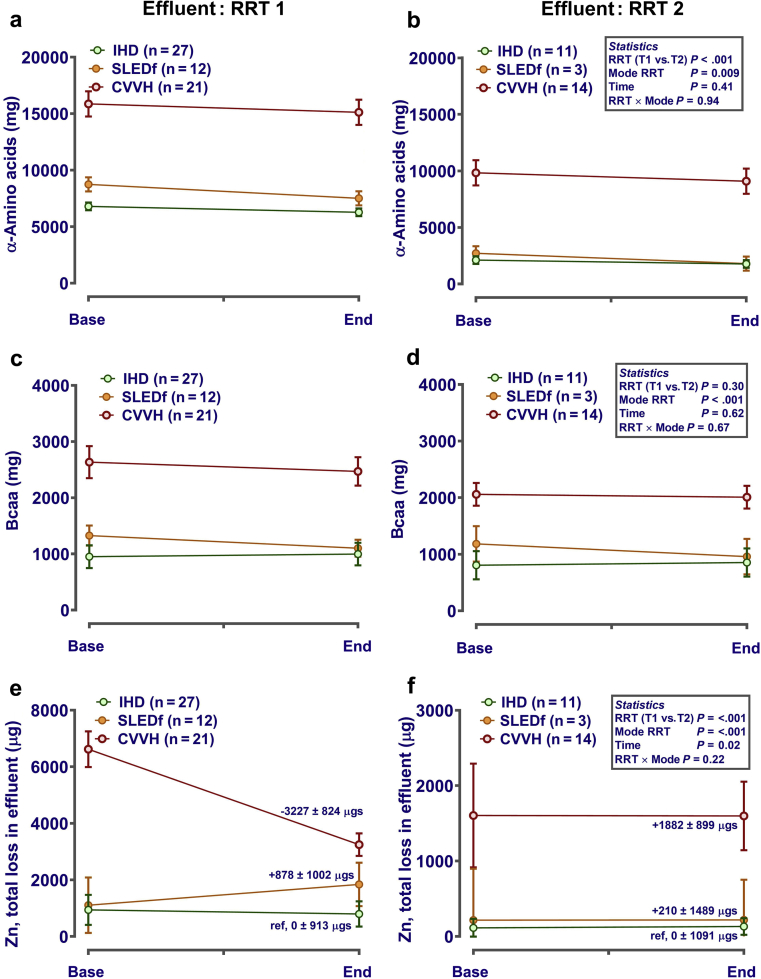
Figure 6.
Comparison of effluent amino acid and trace element loss during the first renal replacement therapy (RRT) session (RRT1) and the second renal replacement session (RRT2). Effluent was sampled before, mid-way through, and at the end of each RRT session. Concentrations of micronutrients were measured in spot samples of baseline effluent (i.e., after “priming” each dialyser; intermittent hemodialysis [IHD], sustained low-efficiency diafiltration [SLED-f]) or in replacement solution (e.g., PrismaSol for continuous veno-venous hemofiltration [CVVH]). Total losses were estimated by multiplying all measured concentrations (μg/l) by the total volume of effluent produced for each patient. Data (mean ± SE) are presented corrected (i.e., included as covariates in the statistical model) for dose-of-dialysis (urea reduction ratio for plasma levels; solute removal index for effluent losses) and plasma concentration (for calculation of effluent losses only). If necessary, data were log10 transformed before statistical analysis to normalize residual error. Graphs were generated in GraphPad Prism 6 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA). Analysis was by repeated-measures analysis of variance or mixed-effect models (Genstat v18; VSNi, Rothampsted, UK), as appropriate, with RRT mode, time, and session as fixed effects. Patient ID was included as a nested random effect. Statistical significance was accepted at P ≤ 0.002 (adjusted for the number of comparisons). bcaa, branched chain amino acids.