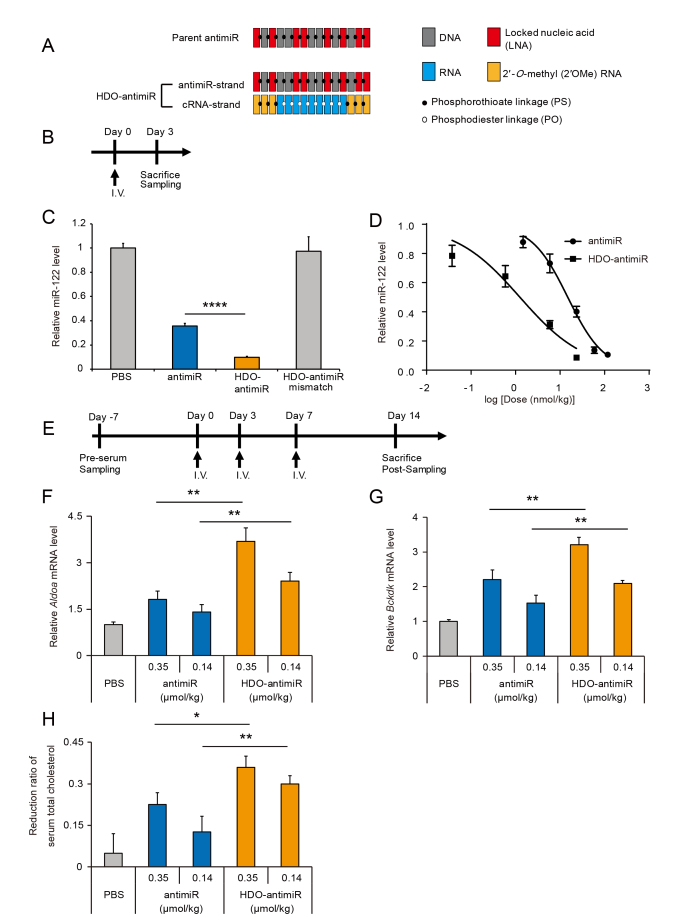
Figure 1.
Enhanced in vivo potency of miRNA-silencing by heteroduplex oligonucleotide (HDO)-antimiR. (A) Design of a DNA/LNA mixmer-type of antimiR and HDO-antimiR. (B) Experimental design for single-injection study. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of relative miR-122 expression in livers from mice treated with the parent antimiR, HDO-antimiR, an HDO-antimiR mismatch, or phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at 24 nmol/kg (corresponding to 0.1 mg/kg as the parent antimiR). (D) Dose–response curve of miR-122 inhibition in livers of mice treated with antimiRs. (E) Experimental design for three-injection study. (F, G) qRT-PCR analyses of relative aldolase A (Aldoa) and branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase kinase (Bckdk) mRNA expression levels which were suppressed by miR-122 in mouse livers after treatment with antimiRs at 0.35 or 0.14 μmol/kg (corresponding to 1.5 or 0.6 mg/kg as the parent antimiR). (H) Reduction ratios of serum total cholesterol relative to those before injections in the same animals (F, G). Mean values ± SEM (n = 5 except for 5.9 and 24 nmol/kg groups in B; n = 9); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001; multiple comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's test.