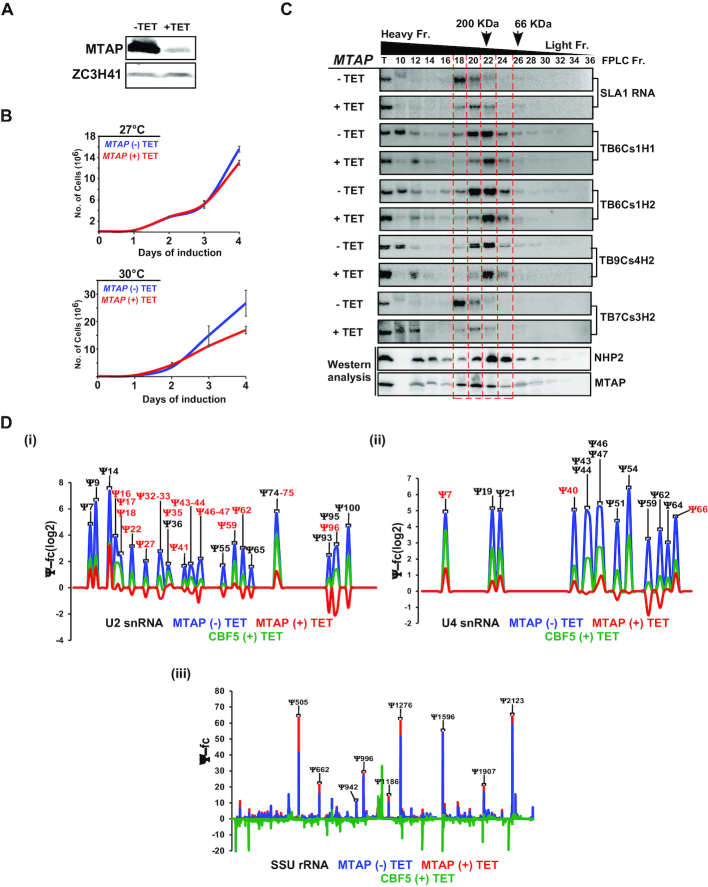
Figure 4.
Ψs on T. brucei snRNAs depend on MTAP. (A) MTAP silencing. (i) Cells carrying the silencing construct for MTAP were silenced for 2.5 days, and protein from (3 × 107) cells was subjected to Western analysis with MTAP antibodies (diluted 1:10 000). (B) Growth of cells upon MTAP silencing. Uninduced cells carrying the silencing construct (-TET) were compared with cells induced for silencing (+TET) at 27°C (upper panel) and 30°C (lower panel). Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. Experiments were done in triplicate (n = 3). (C) snoRNPs are present in two distinct RNP complexes. Whole cell extracts from 109 uninduced (–TET) or induced (+TET) cells carrying the MTAP silencing construct were fractionated on a FPLC Superdex column. Fractions were deproteinized, and RNA was subjected to Northern blot analysis with the indicated RNA probes. Fractions were also subjected to Western analysis. The positions of marker proteins BSA (66KDa) and β amylase (200kDa) in the fractionation are indicated by arrows. The heavy and light fractions are indicated. (D) MTAP silencing abolishes the Ψs only on snRNAs. Ψ-fc(log2) values (y-axis) were determined for MTAP-TET, MTAP +TET and CBF5 +TET based on small RNA Ψ-seq libraries sequenced in the same experiment. Representative line graphs of U2 (i), U4 snRNA (ii) and SSU rRNA (iii). Ψs hypermodified in the BSF stage are shown in red. Four independent biological replicates of small RNA Ψ-seq was used to validate the dependence of T. brucei snRNA Ψs upon MTAP silencing. Ψs from CBF5 and MTAP silencing were compared from the same small RNA Ψ-seq sequencing experiment.