Figure 3.
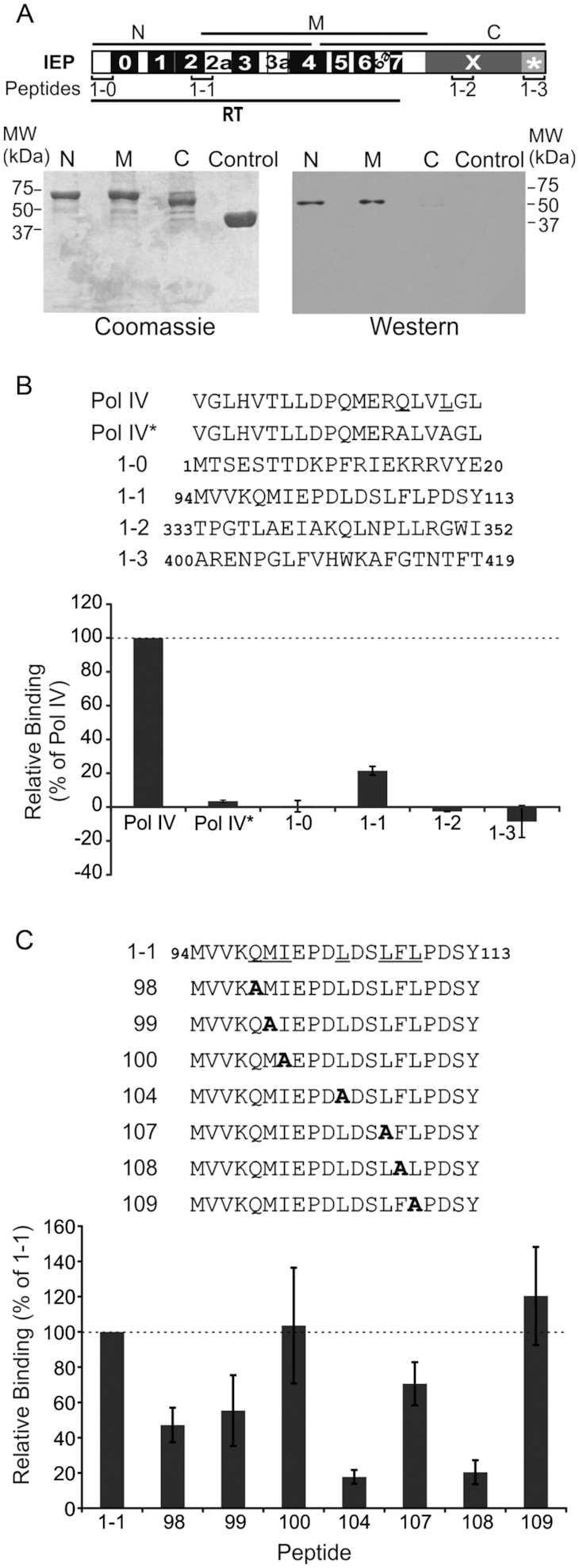
Pulldown assay performed with DnaN and various fragments of the RmInt1 IEP and peptides. (A) Diagram of the various parts of the IEP used in pulldown assays (lower panel). N, N-terminal part of IEP; M, middle region of IEP; C, C-terminal part of IEP; control, MBP. IEP domains are also shown; RT, reverse transcriptase domain with conserved RT sequence blocks (0-7); X, maturase domain; *, C-terminal tail. The positions of the peptides used in panel (B) are also shown. Bottom panel, pulldown assay performed with His-DnaN and various fragments of IEP. The proteins retained were subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue (Coomassie) or subjected to western blotting (western) with antibodies against the His-tag, revealing the presence of His-tagged DnaN in lanes N and M. (B) Peptide binding assay. Sequences of peptides from IEP and DNA polymerase IV used in the assays. Pol IV* has the same sequence as Pol IV except that the two residues underlined in the Pol IV sequence are replaced with alanines. The binding levels are expressed as a percentage relative to the amount of His-tagged DnaN retained by the Pol IV peptide (dashed line). (C) Peptide binding assay with mutant peptides. Sequences of the peptides synthesized, in which the underlined residues of peptide 1-1 have been replace with alanines. Peptides were coupled to streptavidin-coated paramagnetic beads and used to retain His-tagged DnaN. The binding levels are expressed as a percentage relative to the amount of His-tagged DnaN retained by peptide 1-1 (dashed line). In panels B and C, error bars represent standard error of the mean determined from three independent experiments.
