Figure 5.
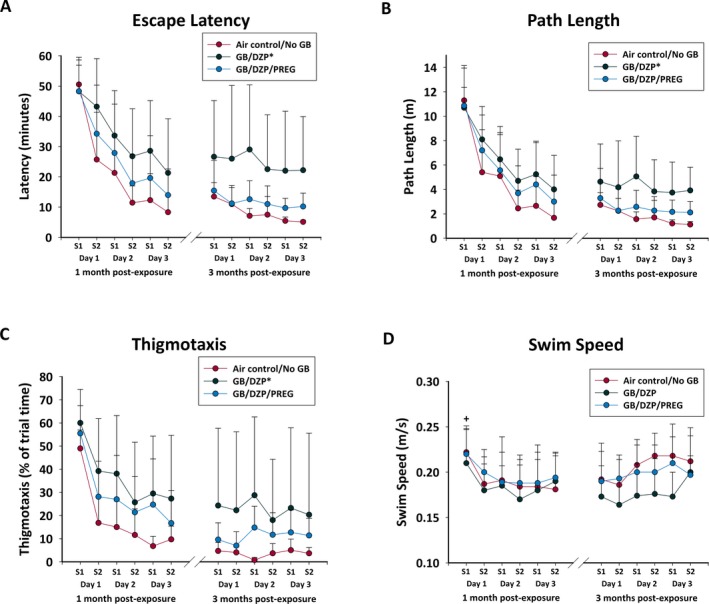
Rats exposed to GB and treated with atropine sulfate and HI‐6 at onset of toxic signs and with diazepam monotherapy (GB/DZP; n = 8) 30 min after seizure onset had impaired performance in Morris water maze test 1 mo after exposure, compared with Air control/No GB (n = 8) shown by (A) increased latency to escape, (B) increased path length (distance travelled), and (C) increased thigmotaxis (perimeter swim). Rats exposed to GB that received pregnanolone and diazepam dual therapy (GB/DZP/PREG; n = 15) were not impaired. All groups improved performance with repeated trials, but the diazepam‐treated GB‐exposed did not perform as well as the air control rats. D, There was no significant effect of GB on swim speed in any group, although all rats had greater swim speed on their first session (S1) compared with their other sessions. Re‐evaluation at 3 mo in a subset of rats showed that the GB/DZP group (n = 6) continued to show greater latency to escape and more thigmotaxis compared with Air control/NoGB (n = 5), while GB/DZP/PREG rats (n = 8) were not impaired. *P < 0.05; +P < 0.05
