Figure 2.
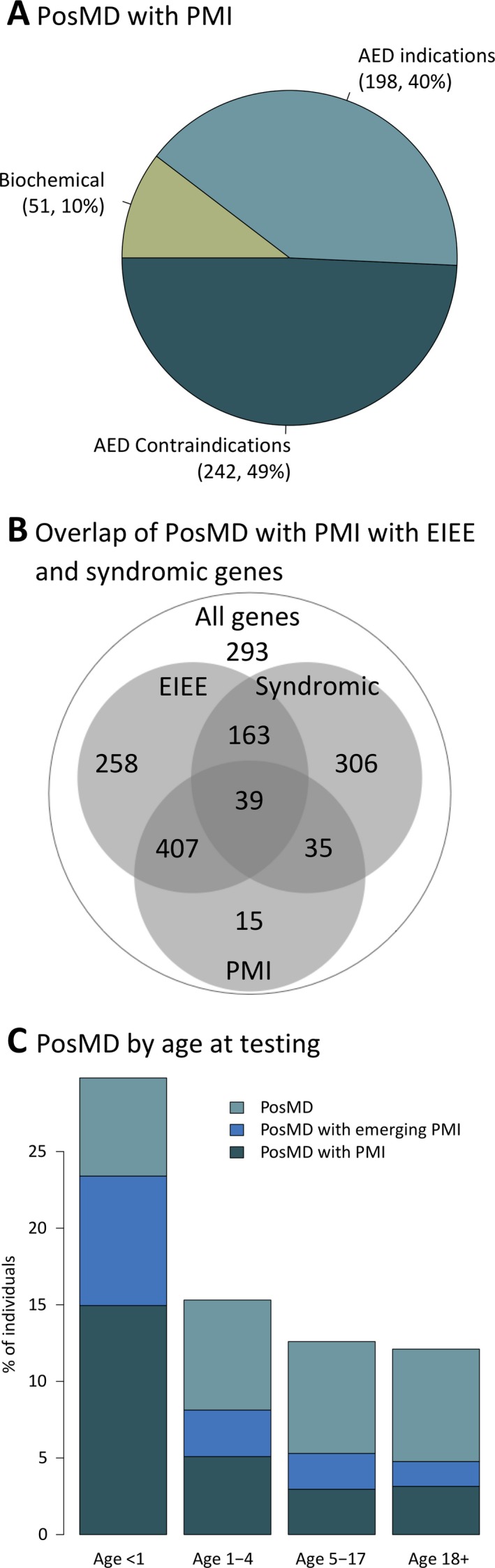
Positive molecular diagnoses (PosMDs) with possible precision medicine implications (PMIs) in epilepsy. Panel A shows the percentage of PosMDs related to various categories of precision medicine in epilepsy. Half of the PosMDs with possible PMI pointed to contraindications for certain anti‐epileptic drugs (AEDs). Approximately 10% of PosMDs with PMI were consistent with biochemical disorders that have established treatment options. Panel B shows the number of PosMDs with PMIs in genes in three overlapping categories of epilepsy disorders: early infantile epileptic encephalopathy (EIEE), Rett/Angelman spectrum of syndromic neurodevelopmental epilepsies, and a third group of all other forms of epilepsy. Panel C shows the positive diagnostic yield in various age groups separated by infancy (age <1 year), early childhood (age 1‐4 years), later childhood (age 5‐17 years), and adulthood (age ≥18 years). Colors indicate the proportion of individuals who received a PosMD with possible PMIs or those with emerging evidence of PMIs. A third group of PosMDs without PMIs is also shown at the top of each column
