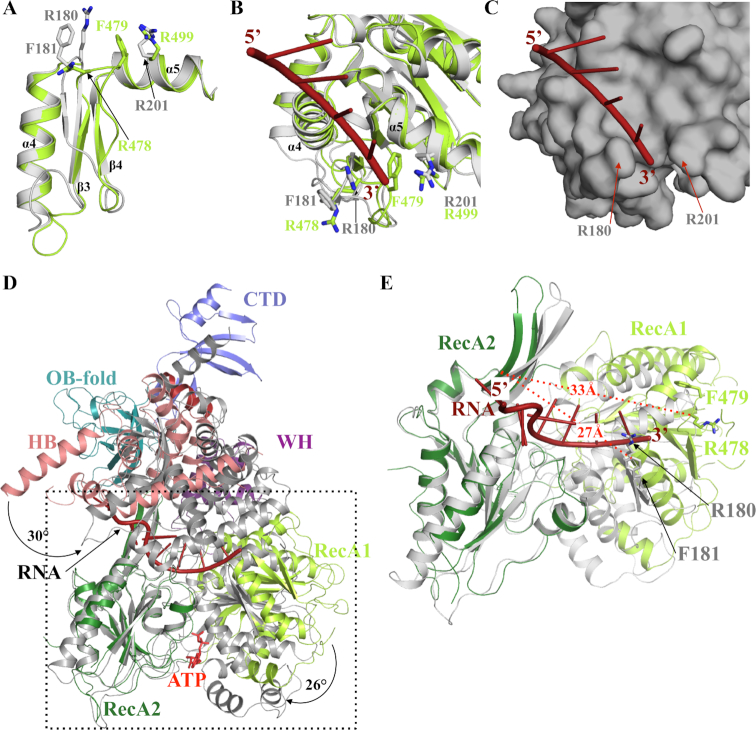
Figure 6.
RNA unwinding mechanism mediated by Dhr1. (A) Superimposition of CtPrp43 (grey) and Dhr1-Hel (light green) 3′ clamp and motif Ib (helix α5) regions from the RecA1 domains. (B) Ribbon representation of ssRNA (red) binding to the RecA1 domain of CtPrp43 (grey; (34)). The superimposed Dhr1 RecA1 domain is shown in light green. The side chains from the 3′ clamp (R180 and F181) as well as R201 from motif Ib that clamp the 3′ end of the ssRNA in CtPrp43 are shown as grey sticks. Equivalent residues from Dhr1 are shown as sticks in light green. (C) Surface representation of ssRNA (red) binding site on the RecA1 domain of CtPrp43 (grey). Same orientation as panel B. (D) Superimposition of Dhr1-Hel apo form onto CtPrp43 RNA•ATP form (gray). The two structures were superimposed using their RecA2 domain as anchor. The ssRNA bound to CtPrp43 is shown in red. (E) Focus on the superimposition of Dhr1-Hel apo form onto CtPrp43 RNA•ATP form (grey; the RecA2 domains were superimposed as in panel D). The side chains from R180 and F181 from CtPrp43 and R478 and F479 from Dhr1 3′ clamp motifs are shown as sticks. The ssRNA bound to CtPrp43 is shown in red. The distances between the 3′clamp (Cα atom of the arginine residue) and the long β-hairpin from RecA2 domain are shown by red dashed lines.