Figure 3.
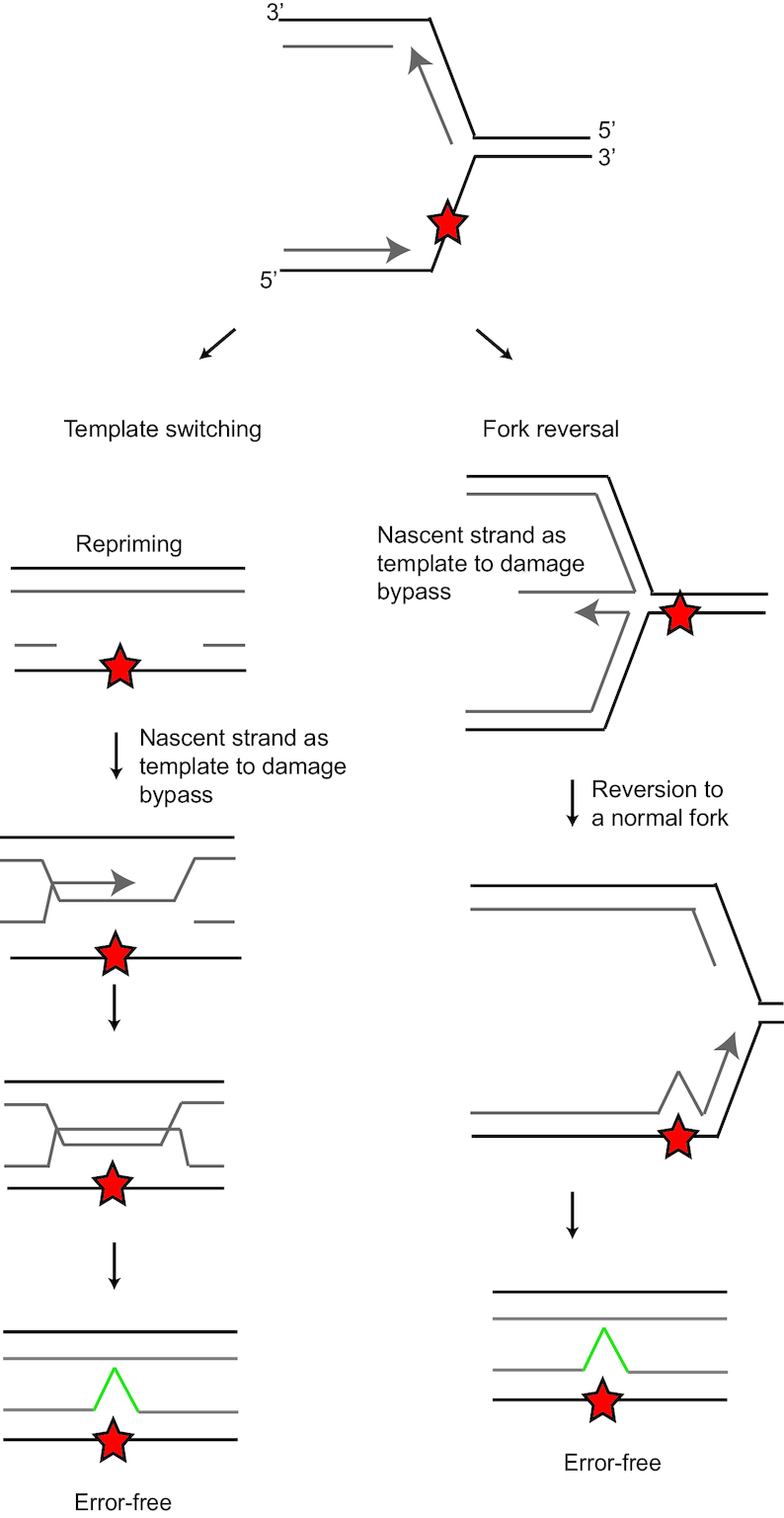
Homology-directed DNA damage tolerance. Homology-directed DDT involves template switching and fork reversal. In order to prevent use of the fork stalling entity as template, the nascent DNA of the sister chromatid is used. Template switching occurs after a priming event in a post replicative gap. After fork stalling, the replication fork can reverse. Fork reversal leads to a chicken foot intermediate structure, which allows access to the nascent DNA of the sister chromatid.
