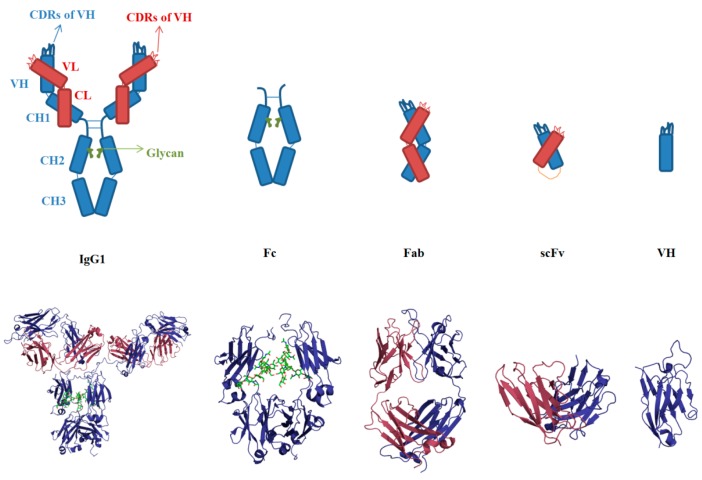
Figure 2.
Molecular architecture of an immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibody and its fragments. An IgG consists of two heavy chains (blue) and two light chains (red). The glycan is presented by the green color. Fc (the crystallizable fragment) is a dimer of CH2, CH3 and glycans. Fab (antigen-binding fragment) is composed of variable heavy (VH) and light (VL) domains, as well as two constant domains (CH1 and CL). ScFv is the artificial format containing VH and VL connected by a flexible linker (yellow). VH (or VL) is the minimal unit for antigen binding mediated by complementarity determining regions (CDRs). The CDR loops in the VH domain are denoted as H1, H2 and H3 (blue); the CDRs in the VL domain are named as L1, L2 and L3 (red). Below are the 3D structures of an HIV neutralizing antibody b12 with intact IgG1, Fc, Fab, scFv and VH formats.