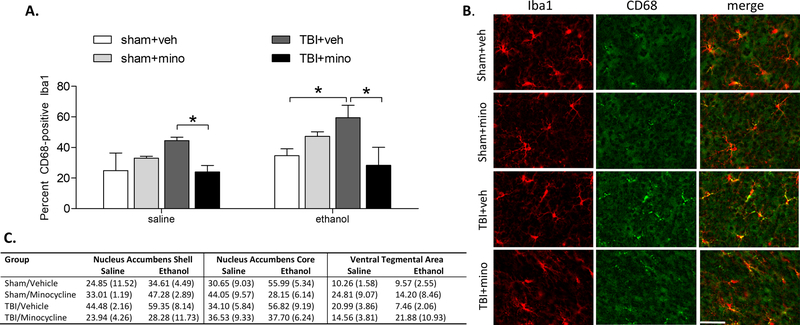
Figure 3. Minocycline inhibited nucleus accumbens shell microglial activation in response to ethanol.
A) TBI significantly increased the percent of Iba1-positive microglia in the nucleus accumbens shell that co-express CD68 following a single IP injection of ethanol. Treatment with minocycline significantly reduced the percent of co-localized Iba1/CD68-positive microglia. B) Representative images of microglia in the ipsilateral nucleus accumbens shell following ethanol injection. Iba1 staining is shown in red, CD68 staining is shown in green. Scale bar = 20 µm. C) The percent of Iba1-positive microglia that co-express CD68 in the nucleus accumbens shell, core, and ventral tegmental area are represented as percent (± one standard error).