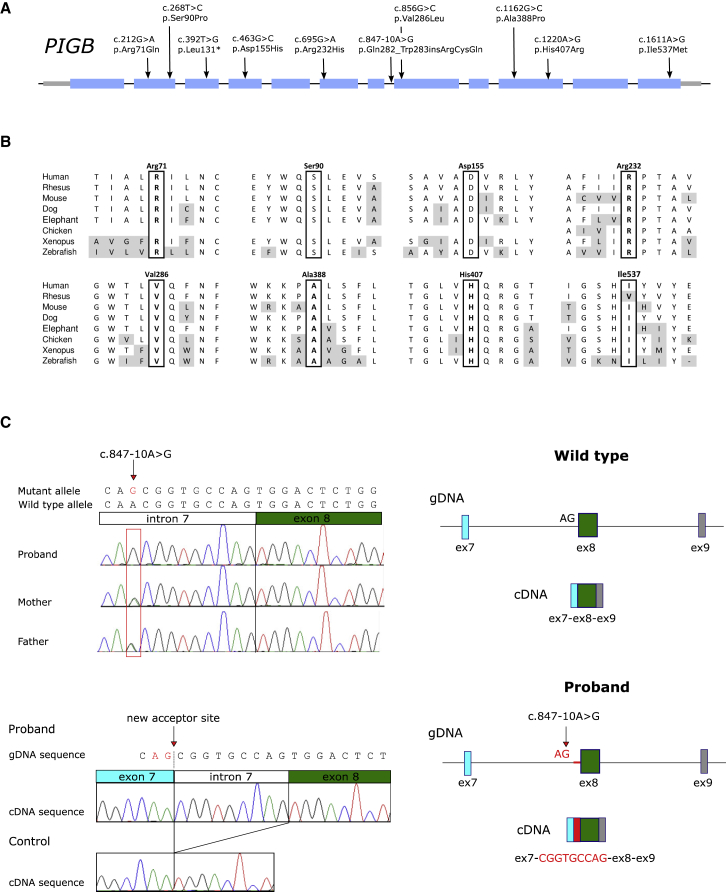
Figure 2.
PIGB Variants
(A) PIGB variants found in affected individuals.
(B) Alignment of the PIGB sequence where missense mutations were found.
(C) Analysis of the PIGB splicing mutation. The upper left depicts Sanger sequencing of proband 6B and the parents that used their genomic DNA showed that the c.847-10A>G mutation was homozygous in the proband and heterozygous in both parents. The lower left depicts the cDNA analysis performed with leukocytes from the proband; the analysis showed the insertion of the last nine bases of intron 7 before the canonical exon 8 as a result of the activation of an aberrant splice acceptor site. The proband did not express wild-type mRNA, which was observed in a control. At right, a graphic description of the activation of the aberrant splice acceptor site at exon 8 in PIGB occurred in the proband. Abbreviations are as follows: gDNA = genomic DNA and Ex = exon.