Figure 5.
Functional Analysis of the Mutant PIGB cDNAs Found in the Families
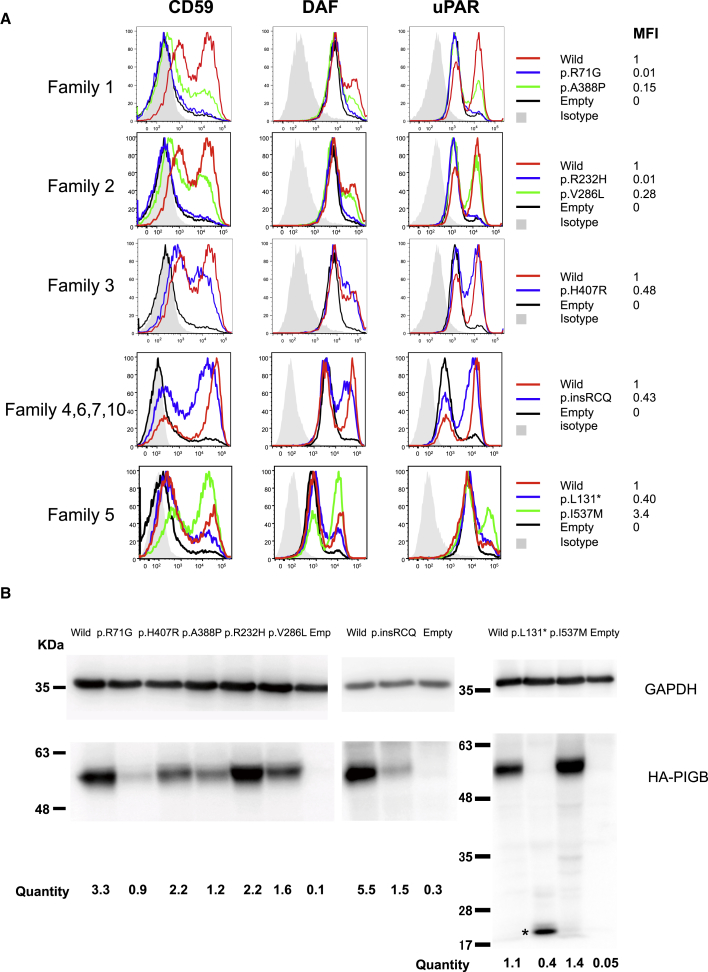
(A) PIGB-deficient CHO cells were transiently transfected with wild-type and mutant HA-tagged PIGB cDNAs subcloned in pME (strong SRα promoter-driven vector). Restoration of the surface expression of CD59, CD55 (DAF), and uPAR was assessed two days later by flow cytometry. Black lines indicate the empty vector; green and blue lines indicate various types of mutant PIGB; the red line indicates wild-type PIGB; and light gray shadows indicate isotype controls. Various missense variants, except for I537M, driven by a strong promoter only partially rescued the expression of GPI-APs compared to wild-type PIGB.
(B) Levels of the mutant PIGB. Lysates of the transfectants were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. For quantification, levels of PIGB were determined by dividing PIGB band intensities by GAPDH band intensities and luciferase activity to normalize for both loading and transfection efficiencies. ∗ = truncated PIGB. Expression levels of mutant PIGB, except for the p.I5le37Met variant, were decreased to various degrees.