Figure 1.
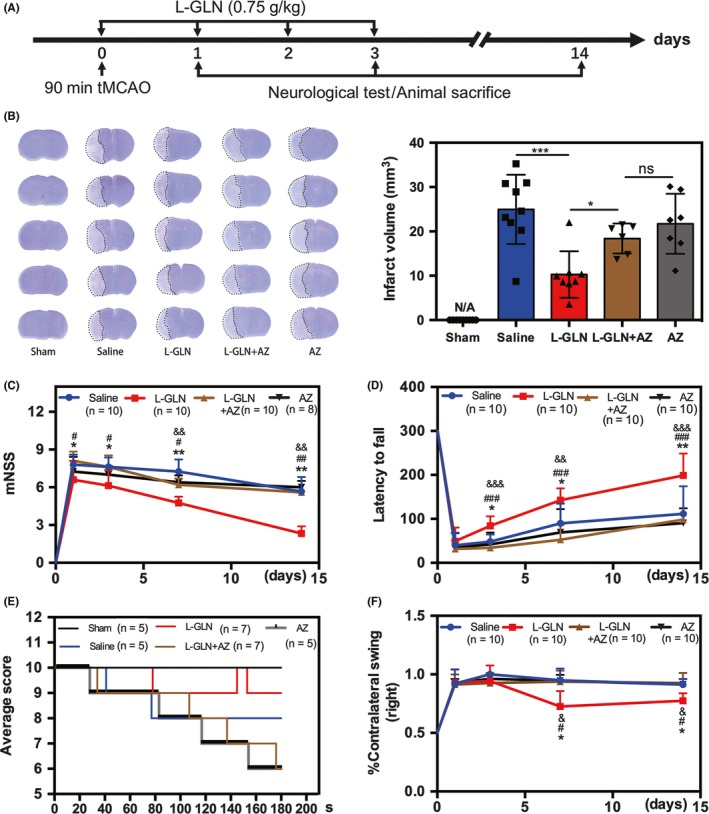
L‐glutamine reduced brain infarct volume and promoted neurobehavioral recovery in mice. A, The experimental scheme. B, Representative cresyl violet‐stained brain sections at 72 h and the statistics of infarct volume of sham (n = 9), saline (n = 9), L‐glutamine (n = 8), L‐glutamine + Apoptozole group (n = 6), and Apoptozole alone group (n = 7), *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Line graphs showed four separate behavioral tests including modified neurological severity score (C), rotarod performance tests (D), hanging wire tests (E), and elevated body swing tests (F), n = 5‐10 per group, from C‐F, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (L‐glutamine group vs. saline group), # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, ### P < 0.001(L‐glutamine group vs. L‐glutamine + Apoptozole group). & P < 0.05, && P < 0.01, &&& P < 0.001(L‐glutamine group vs. Apoptozole alone group). Data are presented as mean ± SD
