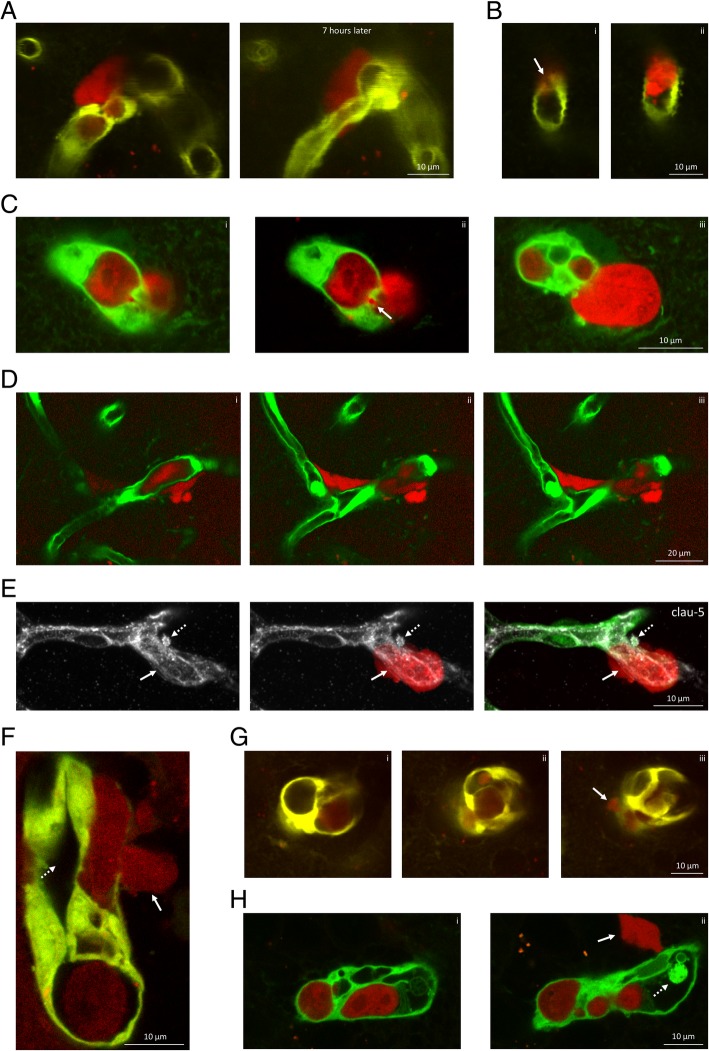
Fig. 3.
Extravasation of triple negative mammary carcinoma cells into the brain. a: Transmigration of a tdTomato-4T1 cell through a small pore in a constricted capillary on day 4 after inoculation of the tumour cells. Representative z-projection of a two-photon micrograph. 7 h later, the extravasation is completed and the tumour cell is attached to the extraluminal surface of the vessel. b: Cross-section representation of the transendothelial migration of a breast cancer cell through a small pore (arrow) on day 4 after inoculation of the tumour cells. The shown two-photon microscopy images (i, ii) are optical sections of the same tumour cell. c: Confocal z-sections (i-iii) of a tumour cell migrating out of a multiluminal vessel on day 4 after inoculation of the tumour cells. Arrow indicates transmigration pore observed on a single optical section (ii). d: Transmigration through a large opening on the vessel wall, as represented in two-photon microscopy z-sections (i-iii). e: Claudin-5 staining (grey) of intact TJs in the neighbourhood of a tumour cell (arrow) extravasating from a cerebral capillary (confocal z-projection). Dashed arrow indicates a claudin-5-positive bleb on the basolateral side of the endothelium. f: Representative two-photon micrograph of a tumour cell (arrow) migrating through the wall of a multiluminal vessel, represented in longitudinal section. Dashed arrow indicates the collateral lumen. g: Two-photon microscopy cross-sections (i-iii) of a capillary having multiple lumens. Arrow indicates extravasating tumour cell. h: Confocal microscopy cross-sections (i-ii) of a capillary having multiple lumens. Arrow indicates extravasating tumour cell. Dashed arrow shows an endothelial plug. Red = tumour cells (tdTomato), green = endothelium (YFP)