Figure 3.
Modeling and Correction of Pathogenic Mutations in Human Cells
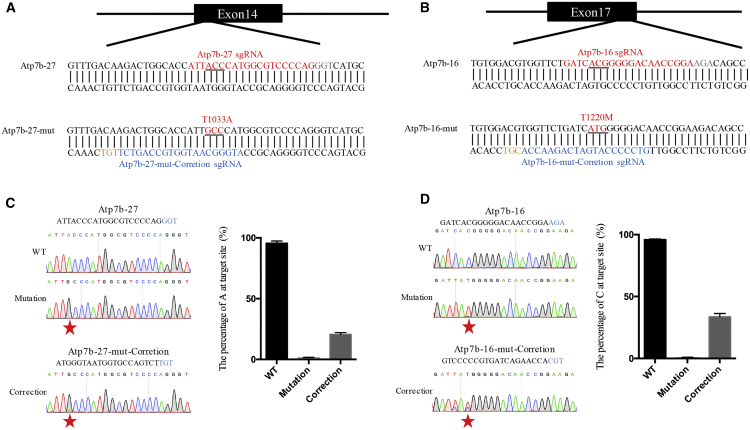
(A) Schematic illustration indicates the sequence and position of the pathogenic site Atp7b-27. The sequence before editing is indicated as Atp7b-27, and the sequence after editing is indicated as Atp7b-27-mut. In the Atp7b-27 sequence, the sgRNA sequence for modeling Atp7b-27 pathogenic mutation is highlighted in red, and the PAM sequence is shown in light gray. In the Atp7b-27-mut sequence, the sgRNA sequence for correcting Atp7b-27 pathogenic mutation is highlighted in blue, and the PAM sequence is indicated in orange. Mutated amino acid codon is underlined and indicated in red in the Atp7b-27-mut sequence. (B) Schematic diagram illustrating the position and sequence of pathogenic site Atp7b-16. The wild-type sequence is shown as Atp7b-16, and the edited sequence is shown as Atp7b-16-mut. In the Atp7b-16 sequence, the sgRNA sequence for modeling Atp7b-16 mutation is highlighted in red, and the PAM sequence is indicated in light gray. In the Atp7b-16-mut sequence, the sgRNA sequence for correcting Atp7b-16 mutation is highlighted in blue, and the PAM sequence is indicated in orange. The mutated amino acid codon is underlined and indicated in red in the Atp7b-16-mut sequence. (C) Modeling and correcting of pathogenic site Atp7b-27. Left: sequence chromatogram of Atp7b-27 in wild-type (WT), mutation, and correction cells. Right: the percentage of target base in wild-type, mutation, and correction cells. Red stars indicate the desired editing. The percentage of each base was calculated using EditR. Data from three independent experiments are indicated as means ± SEM. (D) Modeling and correcting of pathogenic site Atp7b-16. Left: sequence chromatogram of Atp7b-16 in wild-type, mutation, and correction cells. Right: the percentage of target base in wild-type, mutation, and correction cells. Red stars indicate the desired editing. The percentage of each base was calculated using EditR. Data from three independent experiments are indicated as means ± SEM.