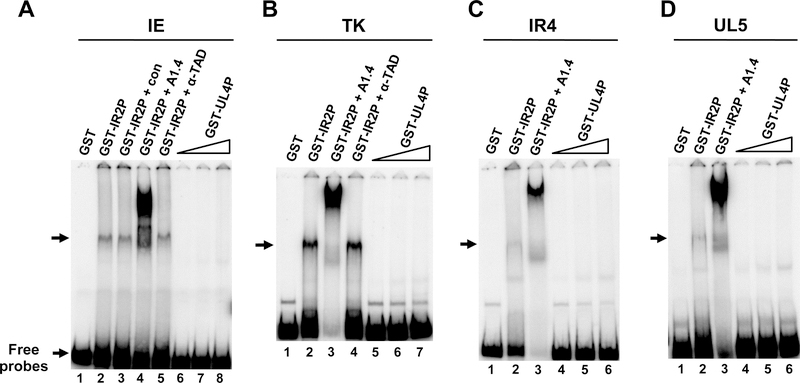
Fig. 2.
Electromobility shift assays examining whether the UL4 protein possesses the ability to bind EHV-1 promoters. A. Immediate-early (IE) promoter DNA (−120/+73); B. thymidine kinase (TK) promoter DNA (−193/+133); C. IR4 promoter DNA (−267/+17); and D. UL5 promoter DNA (199/+20) were radiolabeled and incubated with various amounts of the protein under standard conditions described in Materials and Methods. The amount of GST and GST-IR2P used in this experiment was 100ng. Triangles: increasing amounts of the GST-UL4P added at 1X (100ng), 3X (300ng), 6X (600ng). Control serum (con), IR2P-specific monoclonal antibody (A1.4; Caughman et al., 1995), and IEP TAD-specific polyclonal antibody (a-TAD; Kim et al., 2011) were used. The position of complexes formed by the IR2P is indicated with arrows.