Figure 1.
Spread of GFP-Expressing Exosome-Conjugated AAVs in the Brain
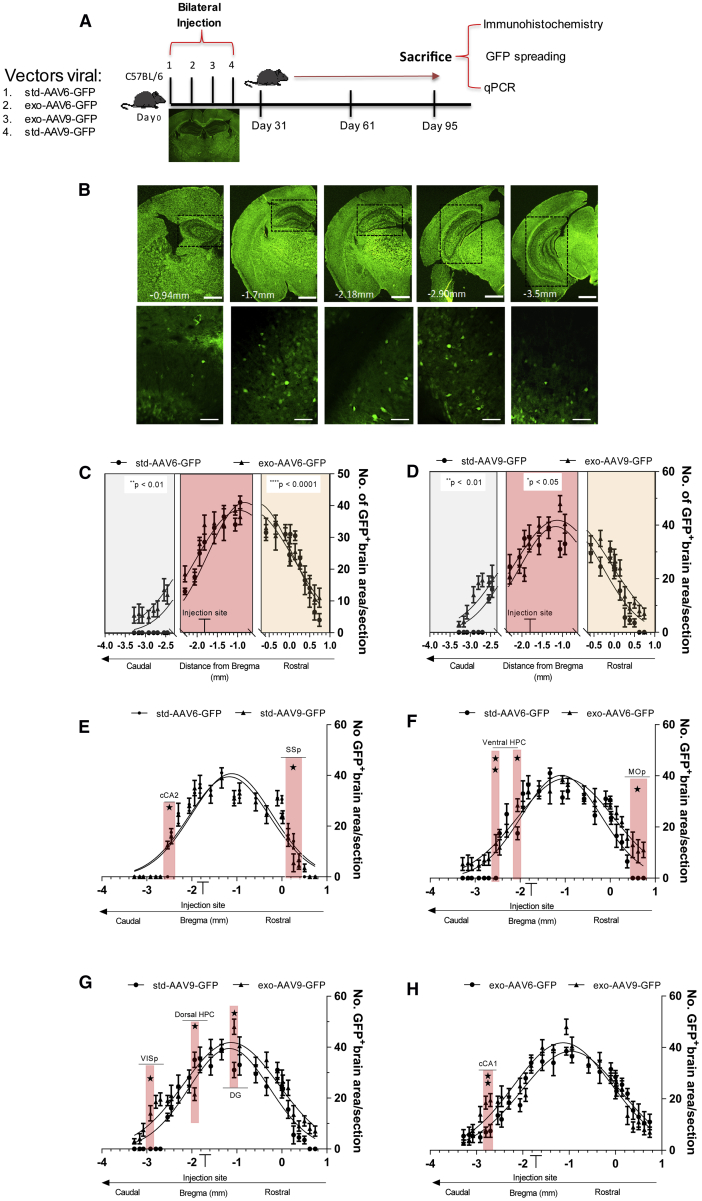
(A) Experimental design of bilateral hippocampus stereotactic delivery of std-AAV6-9 and exo-AAV6-9 vectors (2 μL/injection site) expressing GFP into male C57BL/6J mice sacrificed at 95 days. (B) Coronal brain sections (100 μm)57 (n = 3–5 per group), with representative image of GFP+ cells (50 μm), were randomly chosen, scanned into the computer, and analyzed using a custom-designed Image-Pro-Macro. Fluorescence imaging in coronal brain slices was captured using a Leica DM600B at 5× magnification. (C and D) Gaussian distribution represents the spread within the brain of (C) std-AAV6-GFP (amplitude: 40.9) versus exo-AAV6-GFP (amplitude: 39.5) and (D) std-AAV9-GFP (amplitude 38.5) compared to exo-AAV9-GFP (amplitude: 41.8). (E and F) Sidak’s post hoc comparison revealed significant differences in (E) SSp (p = 0.0104) and cCA2 (p = 0.0261) between std-AAV6 and std-AAV9 and in (F) MOp (p = 0.0366) and ventral HPC (p = 0.0249; p = 0.0049) between std-AAV6 and exo-AAV6. (G and H) Significant difference in DG (p = 0.0116), dorsal HPC (p = 0.0153), and VISp (p = 0.0341) between std-AAV9 and exo-AAV9 and (H) in cCA1 (p = 0.0066) between exo-AAV6 and exo-AAV9. The x axis shows approximate distance from bregma (mm). cCA1, posterior hippocampus CA1; cCA2, posterior hippocampus CA2; DG, dentate gyrus; dorsal HPC, dorsal hippocampus; MOp, primary motor cortex; SSp, primary somatosensory cortex; ventral HPC, ventral hippocampus; VISp, primary visual cortex. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.