Figure 1.
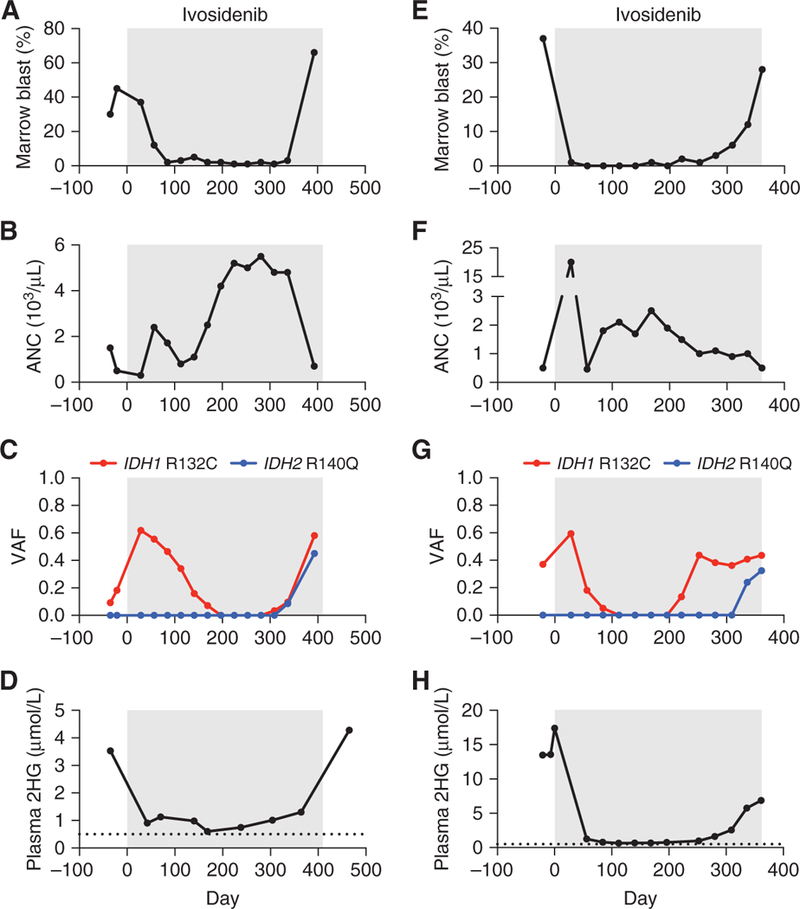
Acquired resistance to mutant IDH1 inhibition associated with emergence of oncogenic IDH2 mutations in AML. Clinical and laboratory features of two patients (case 1 = A–D; case 2 = E–H) with IDH1 R132C-mutant AML treated with the mutant IDH1 inhibitor ivosidenib (gray boxes), including A, E, bone marrow blast percentage; B, F, absolute neutrophil count (ANC); C, G, variant allele frequency (VAF) for IDH1 and IDH2 mutations identified by targeted NGS of bone marrow cells; and D, H, plasma 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG) concentration measured by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Dotted line indicates limit of detection.
