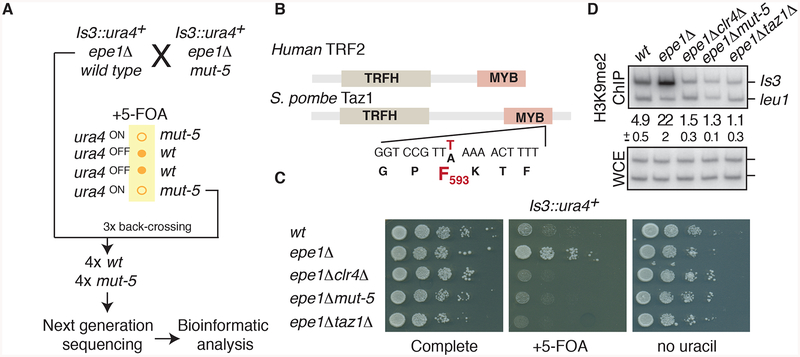
Figure 2. The mut-5 phenotype is associated with a mutation in the DNA binding domain of the telomere-associated protein Taz1.
(A) Identification of the mut-5 mutation by genome sequencing. The mut-5 phenotype was tracked through a series of backcrosses by assaying for FOA sensitivity of mut-5 Is3::ura4+ cells. (B) The domain structure of Taz1 and its human homologue is indicated together with the sequence substitution found in mut-5 cells. (C and D) The loss of island 3 silencing in mut-5 is phenocopied by taz1Δ. (C) Serial dilutions of the indicated strains on complete media, counter-selective (+FOA) media, and media lacking uracil. (D) ChIP of H3K9me2 at island 3 in the indicated strains. Quantitative duplex PCR was used to compare the relative enrichments of island 3 DNA in H3K9me2-immunoprecipitated and input samples. The average enrichments and standard deviations of three measurements are indicated between the panels. See also Figure S2.