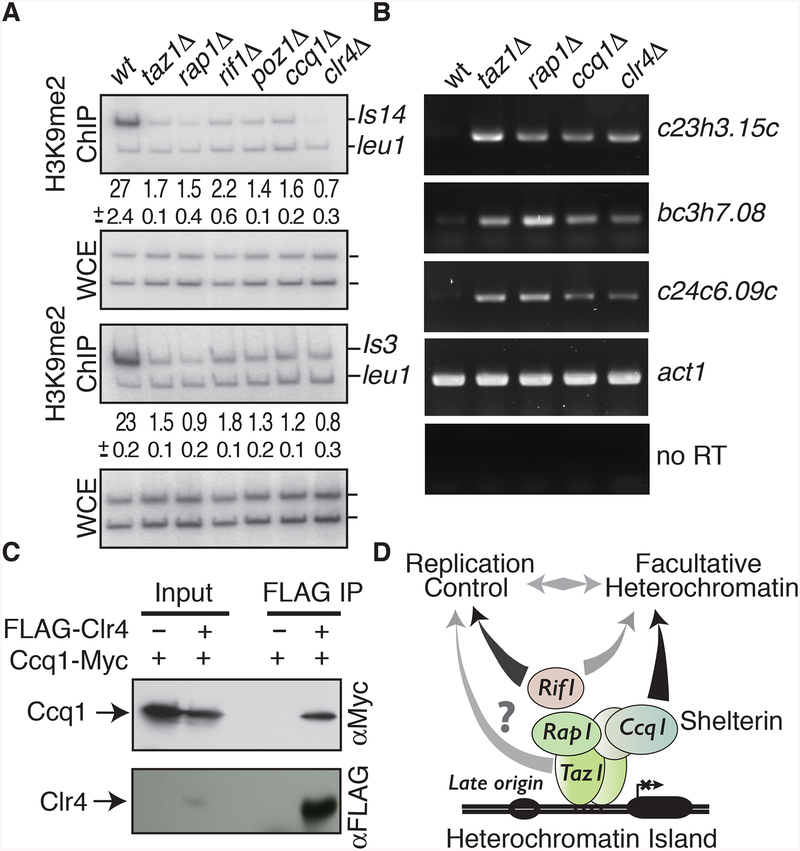
Figure 7. Shelterin components and Rif1 are required for H3K9me at Taz1-dependent islands.
(A) Conventional ChIP combined with duplex PCR was used to assay H3K9me2 at islands 3 and 14. The average enrichments and standard deviations are indicated. (B) Shelterin components affect gene repression at Taz1 targeted islands. RT-PCR was used to examine mRNA levels at Taz1-dependent heterochromatin islands in the indicated strains. act1 mRNA was used as a loading control. (C) The Shelterin component Ccq1 associates with the Clr4 H3K9 methyltransferase, as determined by immunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis. The FLAG-tagged Clr4 co-purifying fraction was probed for Ccq1 and Clr4. (D) Model showing the involvement of Shelterin components and Rif1 in the assembly of facultative heterochromatin islands targeting late origins. Taz1 bound to DNA and other Shelterin subunits, including Ccq1, assemble facultative heterochromatin islands to regulate gene expression and control replication timing. The control of replication timing at Taz1-dependent islands also involves Rif1 (Hayano et al., 2012; Tazumi et al., 2012). Taz1 might also cooperate with additional factors, such as HDAC, to directly affect replication initiation. See also Figure S6.