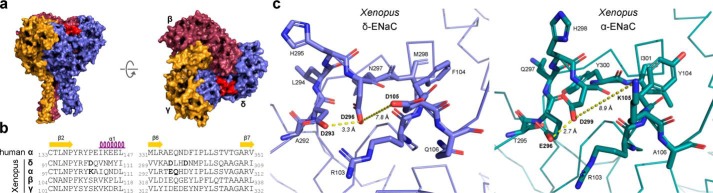
Figure 6.
Comparison of acidic cleft residues in Xenopus δ- and α-ENaC subunits. a, structural arrangement of a Xenopus δβγ-ENaC trimer with the position of the δ-ENaC acidic cleft highlighted in red. b, sequence alignments of human and Xenopus ENaC subunits depicting the β2–α1 and β6–β7 loops that constitute parts of the δ-ENaC acidic cleft. Bold letters indicate acidic cleft residues that have been mutated in this study. c, models of the acidic cleft within Xenopus δ- and α-ENaC. Residues in the acidic cleft are shown as stick representations with the rest of the protein chain depicted as ribbon representations. Contacts between residues in the acidic cleft are highlighted with distances shown.