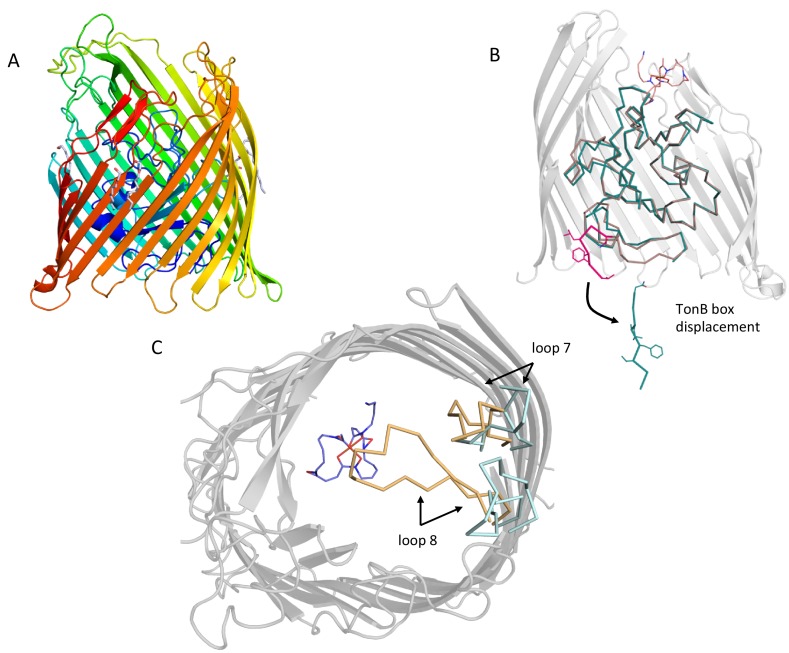
Figure 2. Conformational changes in the plug domain and extracellular loops of FoxA in response to ferrioxamine B and TonB binding.
(A) The overall fold of apo FoxA consists of a 22-stranded β-barrel lined by the small globular plug domain within the lumen. The structure is colour-coded from blue (N-terminus) to red (C-terminus). (B) Structural rearrangements within the plug domain necessary to accommodate interactions with TonBCt. The region of the polypeptide being part of the TonB box common to both FoxA structures is highlighted in pink. This region is displaced by approximately 22 Å into the periplasm. Slight conformational changes are also observed throughout the rest of the plug domain (blue: ternary complex/brown: apo state). (C) Loops 7 and 8 enclose the bound siderophore within the hydrophobic cavity to prevent its dissociation and reduce permeation across the bacterial membrane during the process of siderophore uptake. Loop closure is only evident once the FoxA is bound with ferrioxamine B and the TonBCt fragment (loops coloured brown), indicative of allosteric communication between the extracellular and periplasmic regions of the transporter (blue loops correspond to the apo FoxA).