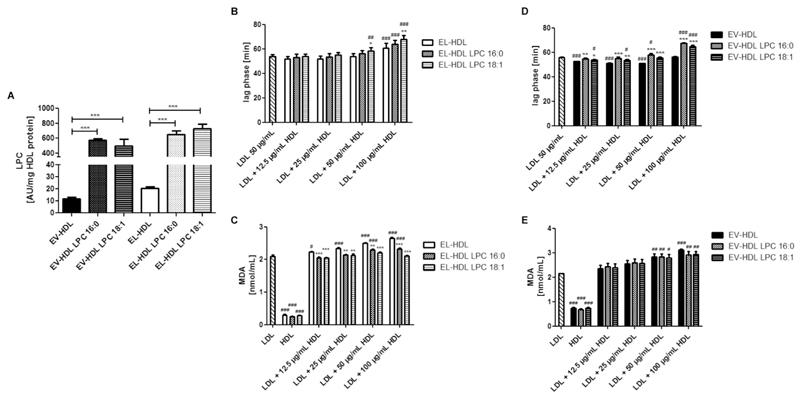
Fig. 5. Impact of LPC enrichment on the antioxidative capacity of EL-HDL.
(A) LPC content of EV-HDL and EL-HDL enriched or not with LPC 16:0 or 18:1 determined by MS. LDL, EV-HDL and EL-HDL (the latter two enriched or not with LPC) were incubated either individually or in the indicated combinations with 2 μmol/L CuCl2 at 37 °C followed by reaction termination after 120 min. (B,D) The formation of conjugated dienes was monitored at 234 nm. (C, E) MDA levels were measured after 120 min by HPLC. Results are means ± SEM of 4 independent modifications of human HDL. The differences in (A) were analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple comparison. The differences between non-enriched and LPC-enriched EV-HDL or EL-HDL (with or without LDL) (B-E) (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001) as well as the differences between EV-HDL or EL-HDL (with or without LPC enrichment, with or without LDL) and LDL (B-E) (#P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.