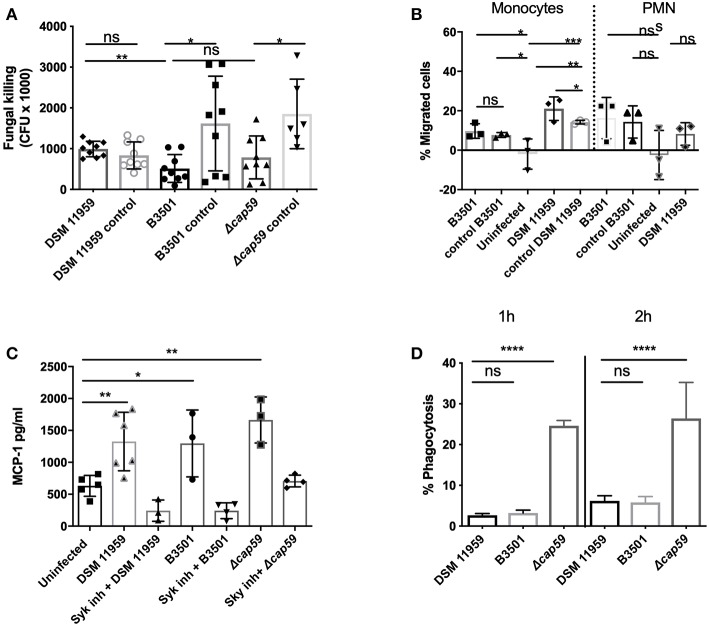
Figure 2.
MC recognition of C. neoformans was mediated by Syk signaling and chemoattracts monocytes. (A) MCs induced killing was serotype dependent. Serotype A (DSM 11959) resisted killing by MCs whereas serotype D (B3501) and acapsular mutant cap59 showed some level of susceptibility. Data from n = 9. (B) Monocytes but not neutrophils were recruited by MCs after C. neoformans infection. The graph depicts the percentage of migration of neutrophil or monocyte migration over time toward supernatants of MCs infected with C. neoformans. (C) MCs secreted MCP-1 in a Syk dependent manner after 20 h infection with C. neoformans (MOI 5). MCP-1 was measured by ELISA in supernatants of HMC-1 infected with C. neoformans (MOI 5). Data from n = 3 (3). Syk was inhibited by piceatannol 10 μM after infection with HMC-1 infection with C. neoformans strains. (D) Acapsular mutants induce significantly more phagocytosis after 1 and 2 h infection. MC phagocytosis of C. neoformans was determined by FACS as the percentage of IgG-Alexa-488 dye high/IgG-Alexa-633 low Cryptococcus cells. Data from n = 4. Significance was analyzed by multi-comparison using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test in (B,D). For (A,C) significance was analyzed using unpaired t-test with Welch correction. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001; ns, not significant.