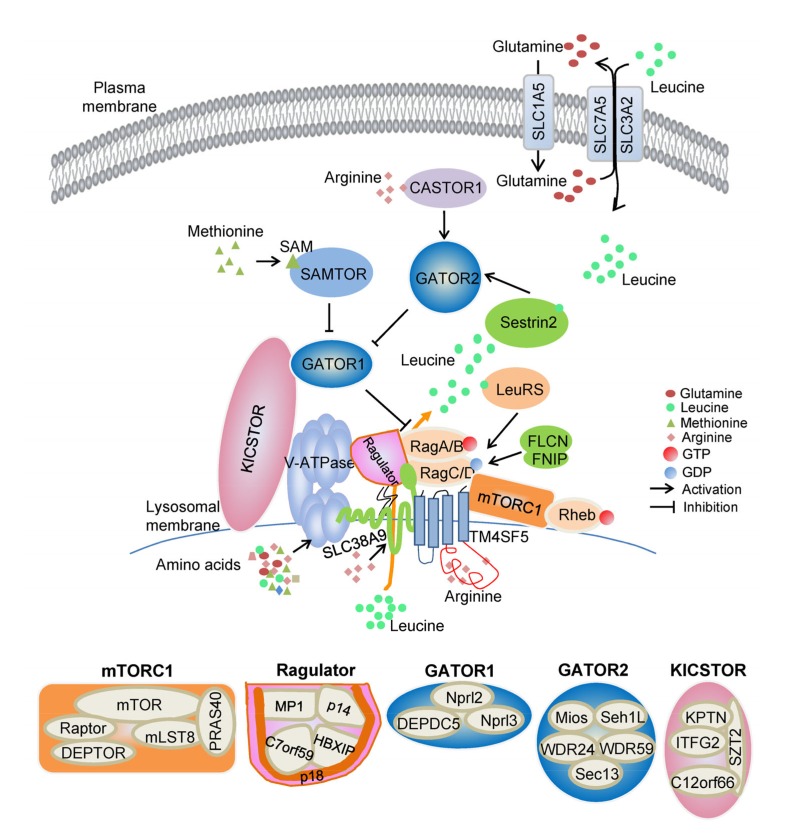
Fig. 1.
Sensors for the mTORC1 pathway regulated by amino acids
Schematic shows amino acid-sensing pathway upstream of mTORC1, including several complexes that control Rag GTPases, and amino acid sensors Sestrin2, LARS, CASTOR1, SLC38A9, and TM4SF5, as well as SAM sensor SAMTOR. mTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; SLC1A5: solute carrier family (SLC) 1 member 5; CASTOR1: cellular arginine sensor for mTORC1 protein 1; SAM: S-adenosylmethionine; SAMTOR: SAM sensor upstream of mTORC1; V-ATPase: vacuolar H+-adenosine triphosphatase; FLCN: folliculin; FNIP: FLCN-interacting protein; LARS: leucyl-tRNA synthetase; TM4SF5: transmembrane 4 L six family member 5; Raptor: regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; DEPTOR: dishevelled, Egl-10 and pleckstrin (DEP) domain containing mTOR-interacting protein; mLST8: mammalian lethal with SEC13 protein 8; PRAS40: proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa; MP1: mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase 1 binding partner 1; HBXIP: hepatitis B virus X-interacting protein; GATOR1/2: GAP activity toward the Rag GTPases 1/2; Nprl2: nitrogen permease regulator 2-like protein; DEPDC5: DEP domain containing 5; Mios: meiosis regulator for oocyte development; Seh1L: Sec13-like protein; WDR24: WD repeat-containing protein 24; KICSTOR: named for kaptin (KPTN), integrin-α FG-GAP repeat-containing protein 2 (ITFG2), C12orf66, and seizure threshold 2 (SZT2)-containing regulator of mTORC1; GTP: guanosine triphosphate; GDP: guanosine diphosphate