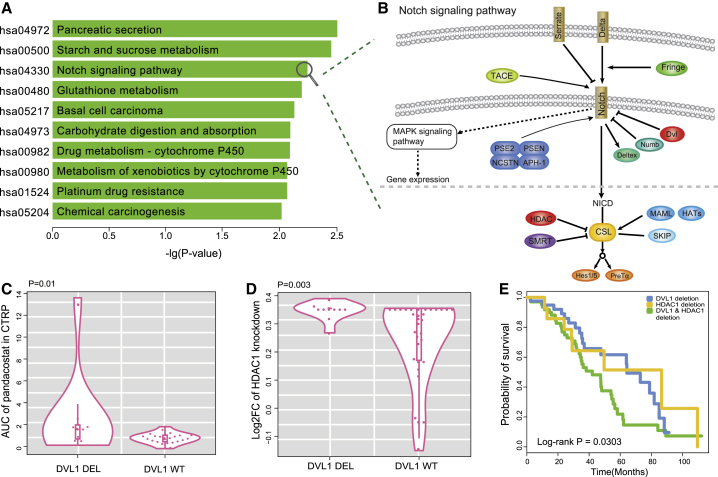
Figure 5.
Functional Analysis of Drug-Resistance-Related SV Interactions
(A) KEGG pathways enriched with the partner genes of HDAC1 in the SV interaction network. The y axis represents significantly enriched pathways, and the x axis is the negative log10-transformed hypergeometric test p value. (B) Notch signaling pathway. The pathway is composed of receptors, ligands, and the CSL DNA-binding protein. DVL1 is located in functional extracellular domains, acting as an inhibitor for Notch receptors, and HDAC1 plays a key role in regulating transcriptional activity by inhibiting CSL. (C) Deletions of DVL1 were related to pandacostat resistance in cell lines compared to wild-type DVL1 (p = 0.01, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). (D) Deletions of DVL1 showed higher viability in HDAC1 knockout cell lines compared to wild-type DVL1 (p = 0.003, Wilcoxon rank-sum test). (E) The Kaplan-Meier overall survival analysis of patients in three groups as follows: HDAC1 deletion, DVL1 deletion, and HDAC1 and DVL1 deletion (p = 0.0303, log-rank test).