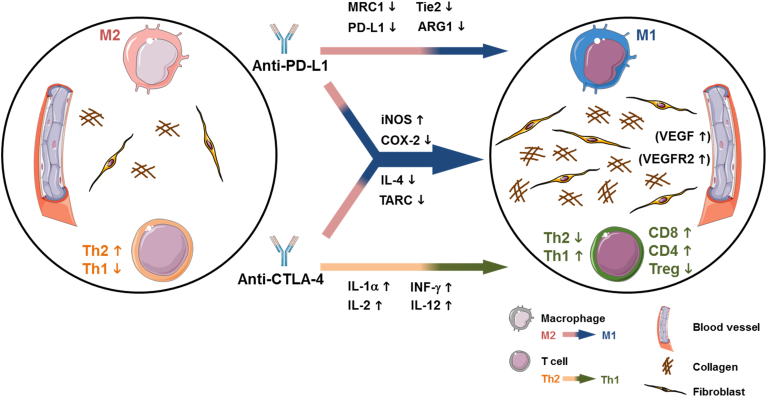
Figure 6.
Suggested mechanism of the synergistic inhibitory effects of dual CTLA-4 and PD-L1 blockade on growth and metastasis of the orthotopic CT26 colon tumors. Anti-CTLA-4 antibodies lead to an increase in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells and a decrease in Treg cells accompanied by a pro-inflammatory Th1 response associated with increased expression of IL-1α, IFN-γ, IL-2, and IL-12. PD-L1 blockade induces a switch to pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages associated with decreased MRC-1, PD-L1, Tie2 and ARG1 expression. Additional synergistic effects of combined CTLA-4 and PD-L1 blockade on the immune microenvironment are obvious by the strongest increase in iNOS expression and the strongest reduction in COX-2, IL-4 and TARC expression. Moreover, dual immune checkpoint blockade induces a stromal reaction with significantly increased fibroblast accumulation and collagen deposition and a slight increase in VEGF-A and VEGFR2 expression which can either indicate stable disease or a compensatory reaction of the tumor to induce therapy resistance. This figure was created with images adapted from Servier Medical Art by Servier. Original images are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.