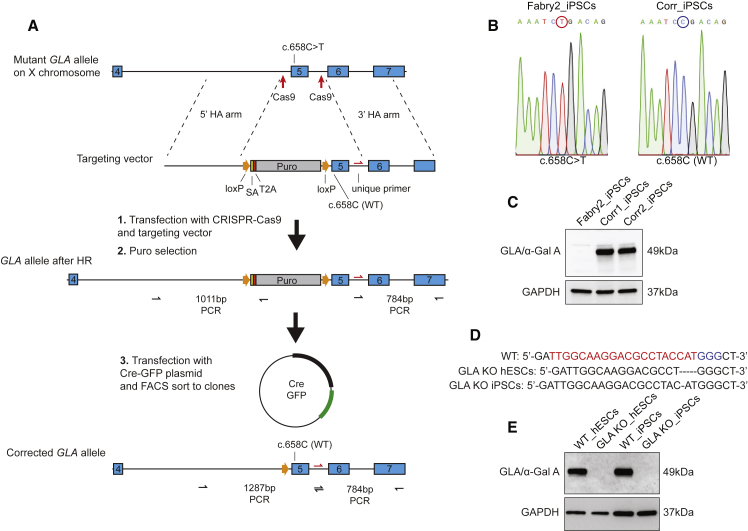
Figure 6.
Genetic Correction of GLA Point Mutation and Generation of GLA Knockouts
(A) Schematic showing the strategy used to correct the GLA c.658C > T mutation and the three main steps: CRISPR-mediated knockin, selection, and removal of selection. Successful homologous recombination and Cre-mediated excision of the selection cassette could be confirmed using the PCR amplicons shown.
(B) Sequence chromatograms across nucleotide c.658 showing successful correction of the mutation.
(C) Western blot showing restoration of α-gal A expression in two sequence-corrected clones.
(D) In-del mutations in GLA introduced into wild-type hESCs and iPSCs for gene knockout. The red and blue nucleotides signify the crRNA and PAM sequences, respectively.
(E) Western blot showing complete knockout of α-gal A expression as a result of the mutations in (D).