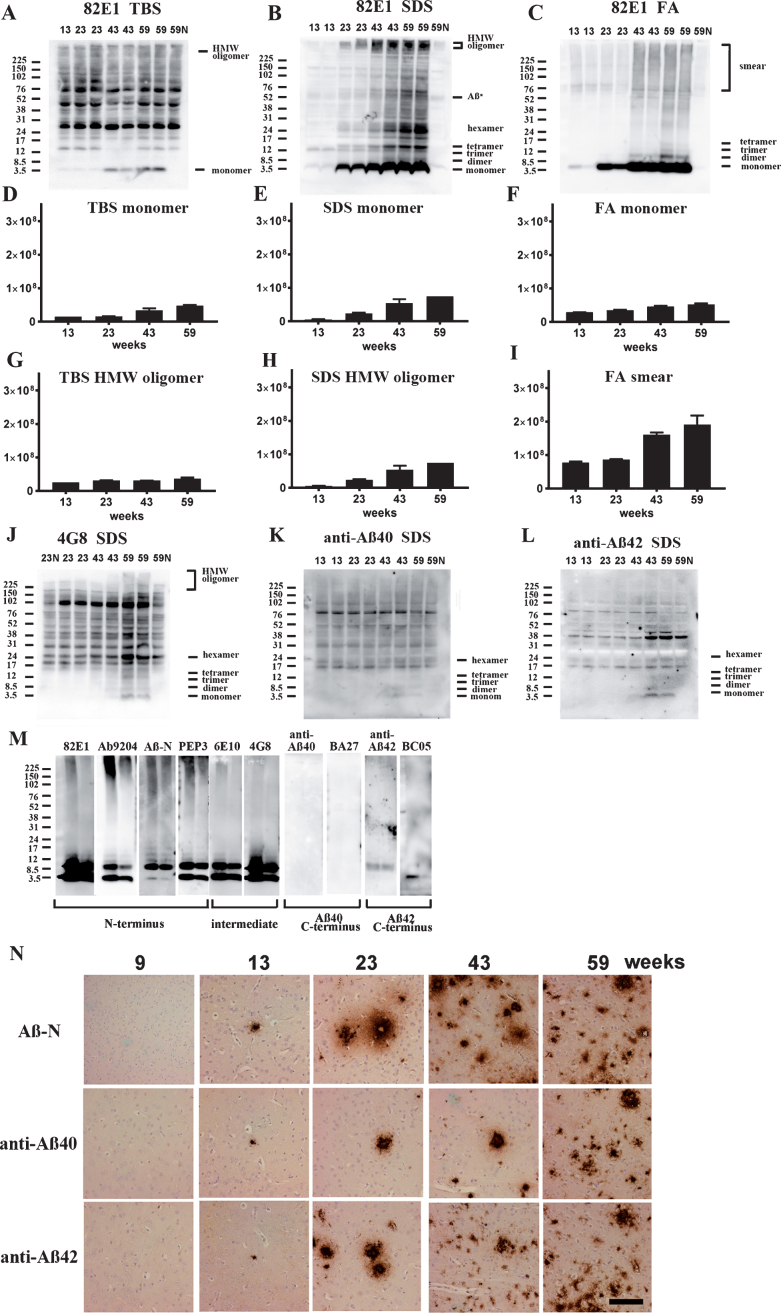
Fig.4.
Age-dependent increase of Aβ monomer and Aβ oligomers in brains of TgCRND8 without an oral immunization trial (A–L), antibody epitope mapping of aggregated synthetic Aβ1–42 (M), and immunostaining of TgCRND8 brains without an oral immunization trial (N). D–I are quantification of Aβ monomer in each fraction (D–F), HMW oligomers in TBS and SDS fraction (G, H), and Aβ smear in the FA fraction (I). 59N indicates nontransgenic littermates at 59 weeks. A) In TBS fractions, Aβ monomers were detected by 82E1 from 13 weeks and the amount increased with age (D). Other molecular weight oligomers except HMW oligomers (G) were difficult to detect because of the existence of mouse IgGs. B) In SDS fractions, Aβ monomers and AβOs, including di-, tri-, tetra-, and Aβ*56, and HMW AβOs, were visualized from 13 weeks. Respective species increased with age (E, H). C) In FA fractions, Aβ monomers from 13 weeks, Aβ dimers from 43 weeks, and diffuse smear patterns from 43 weeks were found (F, I). J–L) 4G8, anti-Aβ40, and anti-Aβ42 weakly detected LMW AβOs, but could not detect HMW AβOs. M) HMW AβOs were detected by antibodies against the N-terminus (82E1, Ab9204, Aβ-N, and PEP3), and were weakly detected by antibodies against the mid portion of Aβ (6E10 and 4G8), but were not detected by anti-Aβ42 and BC-05. Anti-C-terminus to Aβ40 (anti-Aβ40 and BA-27) did not detect Aβ1–42. N) Immunostaining of TgCRND8 brains using Aβ-N (1:1000), anti-Aβ40 (1:1000), and anti-Aβ42 (1:400) showed age-dependent Aβ deposition. Aβ burden labeled by anti-Aβ40 and anti-Aβ42 were weaker than those by Aβ-N. Bar represents 100 μm. One mouse at 13 weeks, 2 mice at 23 weeks, 43 weeks, and 59 weeks were used for analysis.