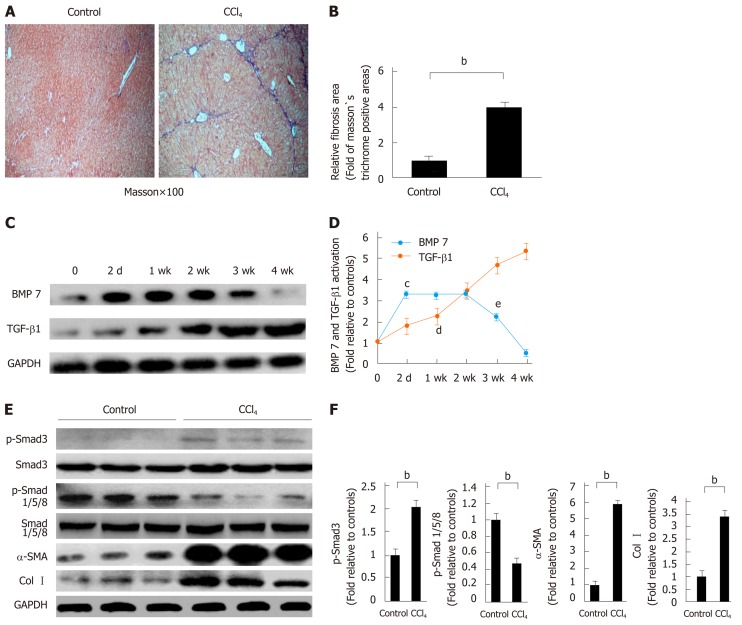
Figure 1.
Decreased bone morphogenetic protein 7 and increased transforming growth factor-beta 1 in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrotic mice. Mice were challenged by intraperitoneal injections of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) or control vehicle (Control, corn oil as the vehicle) as described in Materials and Methods. The severity of liver fibrosis was evaluated by using the measures, including A: Masson’s trichrome staining of fibrotic areas (by collagen deposition, 100×); B: Morphometric analysis of fibrotic lesions in the liver; C: Western blot analysis of expression of BMP7 and TGF-β1. At the indicated time points after CCl4 injection (2 d, 1 wk, 2 wk, 3 wk, and 4 wk), equivalent amount of whole liver detergent lysates were blotted for detecting BMP7 and transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1). The level of BMP7 protein expression first rose and then fell, which significantly decreased at 4 wk, while TGF-β1 expression showed a gradual upward trend; D: Trend chart of BMP7 and TGF-β1 protein expression in liver-injured mouse model induced by CCl4. cP < 0.01 or dP < 0.01 compared to time point 0, eP < 0.05 compared to time point 2 wk; E: Western blot analysis of expression of p-Smad3, p-Smad1/5/8, α-SMA, and Col I. At the time point 4 wk, equivalent amount of whole liver detergent lysates were blotted for detecting p-Smad3, p-Smad1/5/8, α-SMA (a marker for myofibroblast differentiation), and Col I. Each lane represents one individual mouse. GAPDH was used as a loading control; and F: Densitometry analysis of the expression of p-Smad3, p-Smad1/5/8, α-SMA, and Col I. Data are pooled and represented as the mean ± SE, n = 8 animals per group. bP < 0.01. BMP7: Bone morphogenetic protein 7; p-Smad3: Phosphorylated Smad3; CCl4: Carbon tetrachloride; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-beta 1; Col I: Collagen I; α-SMA: Alpha-smooth muscle actin.