FIGURE 3.
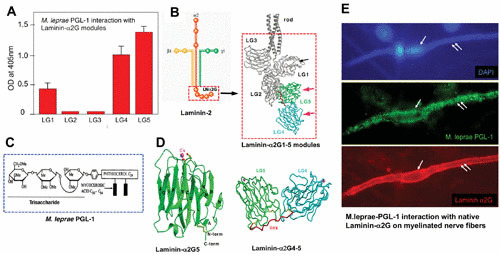
Molecular basis of neural tropism of M. leprae. Interaction of M. leprae-specific PGL-1 on the bacterial cell wall with the tissue-specific α2LG domain on the basal lamina. (A) PGL-1 binding to the recombinant G modules of the α2LG domain. OD, optical density. (B) Subunits of the laminin-2 isoform comprising α, β, and γ chains with the cell-binding α2G domain and its modules α2LG1 to α2LG5. (C) Composition of M. leprae PGL-1. (D) Crystal structure of PGL-1-binding α2LG5 and α2LG4-5 modules of the α2LG domain. (E) M. leprae PGL-1 binding (green) to the native α2LG domain (red) on the basal lamina surrounding a myelinated Schwann cell–axon unit (outer surface of nerve fiber is labeled in red to demarcate the α2G domain) colocalized with PGL-1 (green) when cultures were incubated with a PGL-1 suspension.
