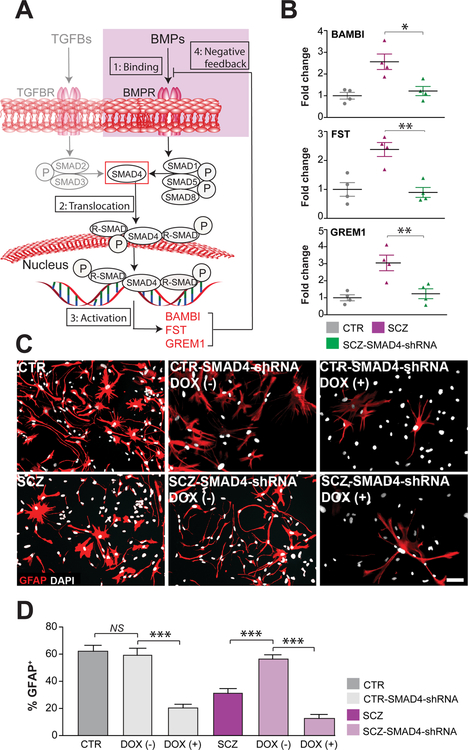
Figure 3. SMAD4 regulated the astrocytic differentiation of SCZ GPCs.
A, SMAD4 regulates the expression of TGFβ and BMP pathway signaling through: 1) phosphorylation of both SMAD2/3 and SMAD1/5/8; 2) SMAD nuclear translocation and activation of target promoters, including the early induction of the endogenous BMP inhibitors BAMBI, follistatin (FST) and gremlin1 (GREM1); and 3) their subsequent feedback inhibition of BMP signals. B, BAMBI, FST and GREM1 were all significantly over-expressed in SCZ CD140a-sorted hGPCs relative to control-derived hGPCs. SMAD4 knockdown in SCZ hGPCs (4 SCZ lines, 3 repeats/line) then repressed the expression of BAMBI, FST and GREM1 to control levels. C, SMAD4 knockdown in SCZ hGPCs restored astrocytic differentiation to that of CTR hGPCs (4 SCZ lines, 3 repeats/each line). DOX (−)/(+) means short-term/long-term culture with DOX. D, SMAD4 knock-down after astrocytic induction, as mediated via continuous doxycycline exposure, caused a loss of GFAP-defined astrocytes in both SCZ and CTR groups. DOX (−)/(+) means short-term/long-term culture with DOX. Scale: 50 μm; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; one-way ANOVA; NS: not significant; mean ± SEM.