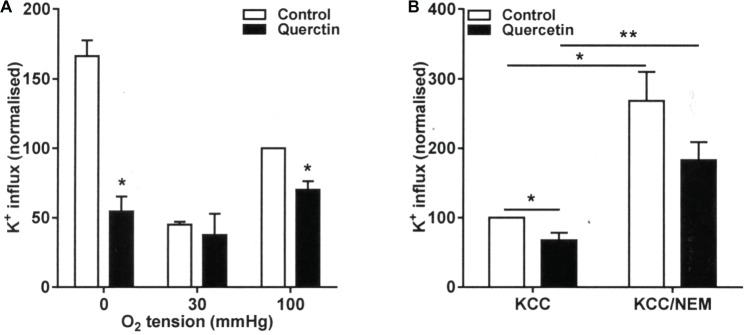
Figure 3.
Effect of quercetin on KCl cotransport (KCC) activity in RBCs from SCA patients. RBCs were pre-incubated for 30 min at 37°C in air without or with quercetin (100 μM) in N-MBS. They were then equilibrated for 20 min in Eschweiler tonometers at the required O2 tension in the continued absence (control) or presence of quercetin. KCC activities, defined as the differences of clotrimazole-insensitive K+ influx in the absence and presence of Cl−, were measured. Ouabain (100 μM) and bumetanide (10 μM) were present in all experiments, and influxes were normalized to those of control RBCs at 100 mmHg. (A) RBCs were pre-incubated for 30 min at 37°C in air without or with quercetin (100 μM) in N-MBS, equilibrated in Eschweiler tonometers and KCC activity measured in the continued absence or presence of quercetin. Histograms represent means ± SEM, n = 3, *p < 0.05, comparing RBCs in the absence and presence of quercetin. (B) RBCs were first pre-incubated in N-MBS without or with NEM (1 mM) for 45 min at 37°C, 20% Hct. Both aliquots were divided and subsequently incubated without or with quercetin for 30 min, after which aliquots were diluted 10-fold into flux tubes and KCC activity measured as described in (A). All incubations were carried out in air. Histograms represent means ± SEM, n = 5. **p < 0.01, comparing RBCs in the groups indicated.