Fig. 3.
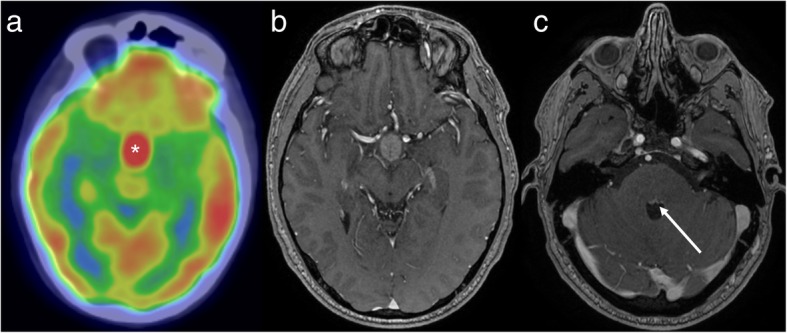
FDG-PET (a) in a patient with systemic lymphoma shows abnormal intracranial uptake (asterisk), consistent with secondary CNS involvement. This is localised to the hypothalamus on the post-contrast MRI (b). The post-contrast MRI (c) also demonstrates more extensive leptomeningeal disease than is appreciable on PET, including along the ependymal surface of the fourth ventricle (arrow)
