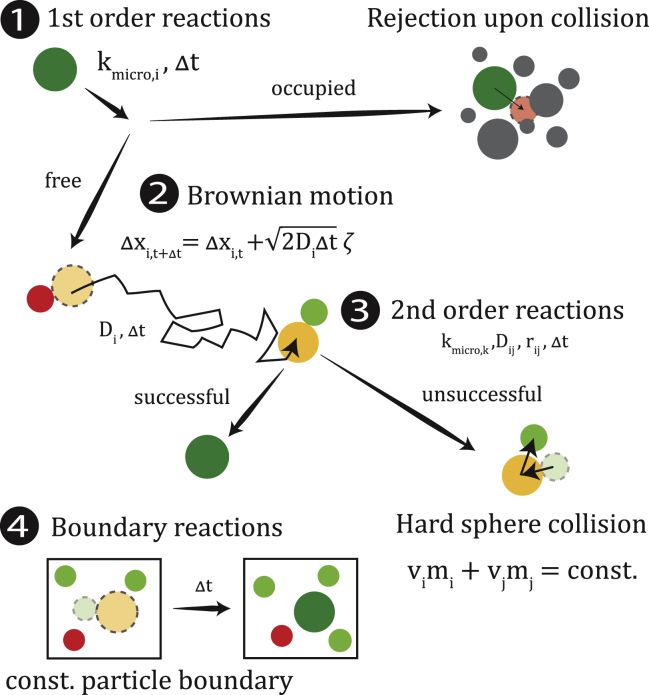
Figure 1.
Individual algorithm steps of the molecular particle model. 1) First-order reactions are determined by a probabilistic success rate depending on the microscopic reaction rate per molecule kmicro,i and the time step Δt. 2) The Brownian motion for every molecule is determined by its individual diffusion coefficient Di. 3) For second-order reactions, success is determined upon collision given the microscopic reaction, the sum of the diffusion coefficient Dij = Di + Dj, the sum of the radii of the colliding particles rij = ri + rj, and the time step (24). 4) Boundary reactions are given as constant particle boundaries, wherein the removal or insertion of particles is done if the number of particles deviates from the given boundary condition.