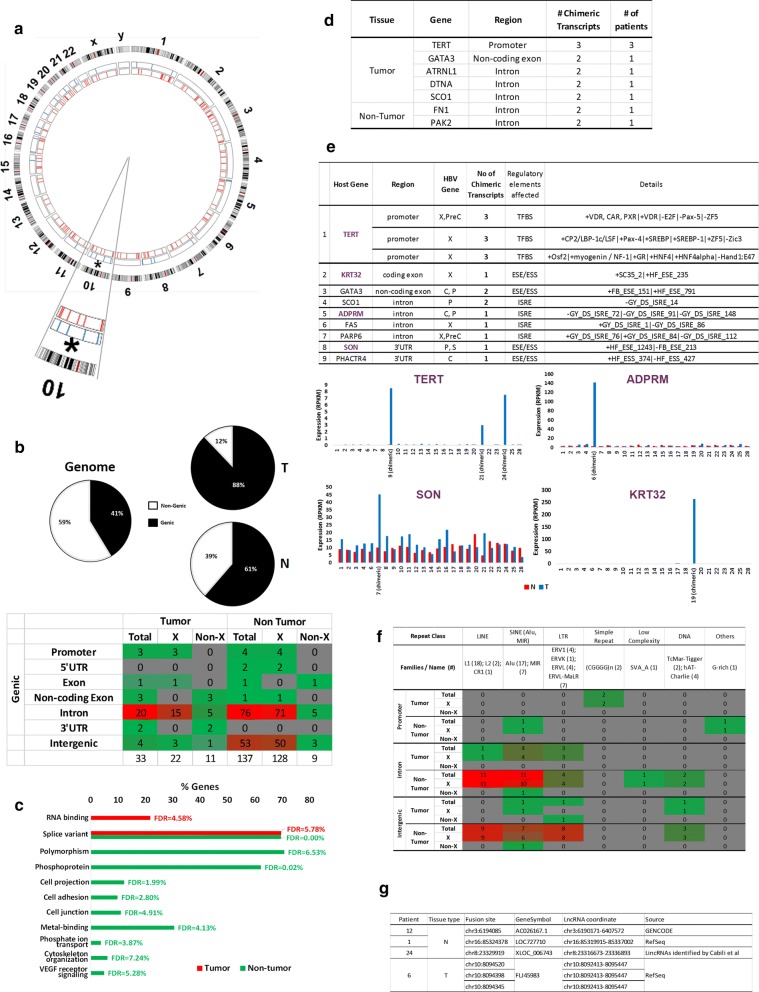
Fig. 4.
Distribution of fusion points on chromosomes. a Circos plot showing the distribution of fusion points on human chromosomes (hg19). Each red or blue bar represents a fusion site on the corresponding chromosome in N and T samples, respectively. b Proportion of fusion sites in genic and intergenic regions. Top panel: The left pie chart shows the proportion of genic and intergenic region in human genome. The two pie charts on the right show the proportion of HBV-host chimeric transcripts from the genic and intergenic regions in T and N samples, respectively. Genic region includes promoters, 5′- and 3′-UTRs, coding or non-coding exons and introns while intergenic region excludes the genic region. Bottom panel: Distribution of fusion points on functional regions of genes. c Functional annotation of genes with viral integration sites in N and T. Red bars represent the functional annotation of genes with viral integration sites identified in the tumor tissues while the green bars correspond to the functional annotation of genes with integration sites in non-tumor tissues. d Table showing genes fused with HBV in at least two chimeric transcripts. e Tumor chimeric transcripts predicted to alter regulatory elements and their association with expression. Top panel: Table showing putative regulatory sites of genes that are predicted to be affected by viral integration in tumor tissues. Genes with fusion sites that are associated with expression changes are in bold purple. Bottom panel: association between tumor chimeric transcripts and host gene or adjacent exon expression. Red bars represent gene/exon expression in non-tumor while blue bars represent expression in tumor tissues. f Distribution of fusion points in different classes of repeat regions. g Distribution of fusion points in long non-coding RNAs