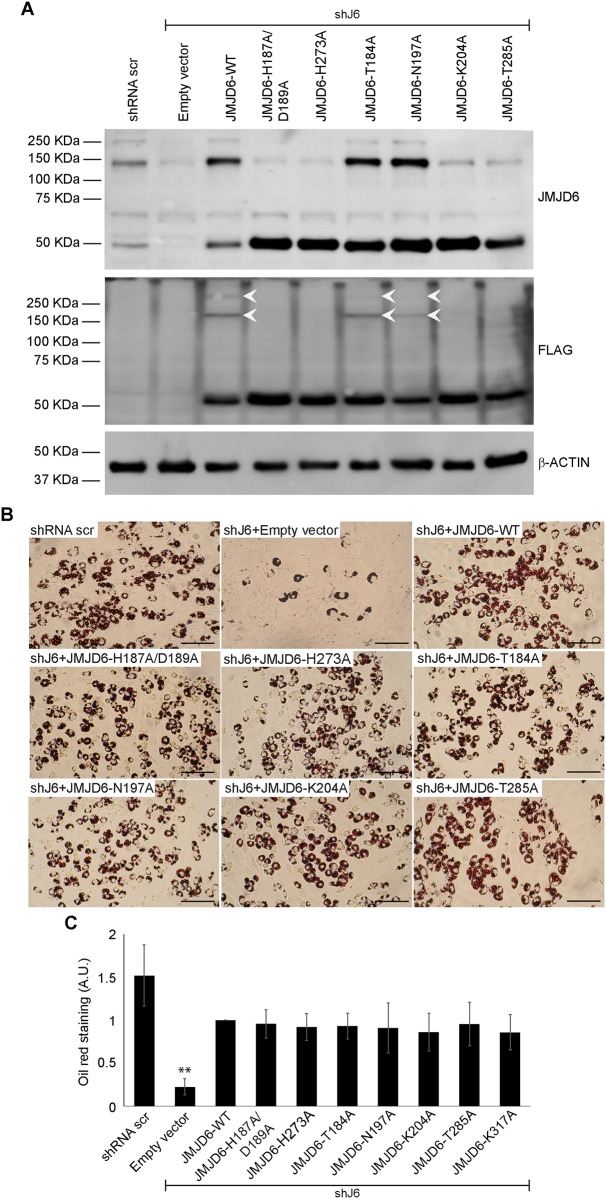
Fig 2. Expression of catalytically deficient JMJD6 mutants rescues the adipogenic differentiation deficiency caused by JMJD6 knockdown.
(A) Representative western blots for JMJD6 or ectopically expressed JMJD6 (FLAG) in C3H10T1/2 cells with stable knockdown of JMJD6 (shJ6). Controls included cells expressing a scramble shRNA (shRNA scr) that does not affect JMJD6 expression and JMJD6 knockdown cells expressing the empty vector (lanes 1–2). White arrows indicate multimerization of expressed mutants. β-ACTIN levels were monitored as a control. (B) Representative Oil Red O staining of C3H10T1/2 cells with stable expression of either scramble shRNA (shRNA scr) or shRNA against Jmjd6 (shJ6) that were expressing the empty vector or the wild type or the indicated JMJD6 mutants. Staining was performed after 6 days of differentiation. Scale bar = 100μm. (C) Quantification of Oil Red O staining. The values are the average +/- standard deviation of optical density at 500nm of three independent experiments. The data are relative to the value for the JMJD6 wild type sample, which was normalized to 1. **P<0.01; A.U.–arbitrary units.