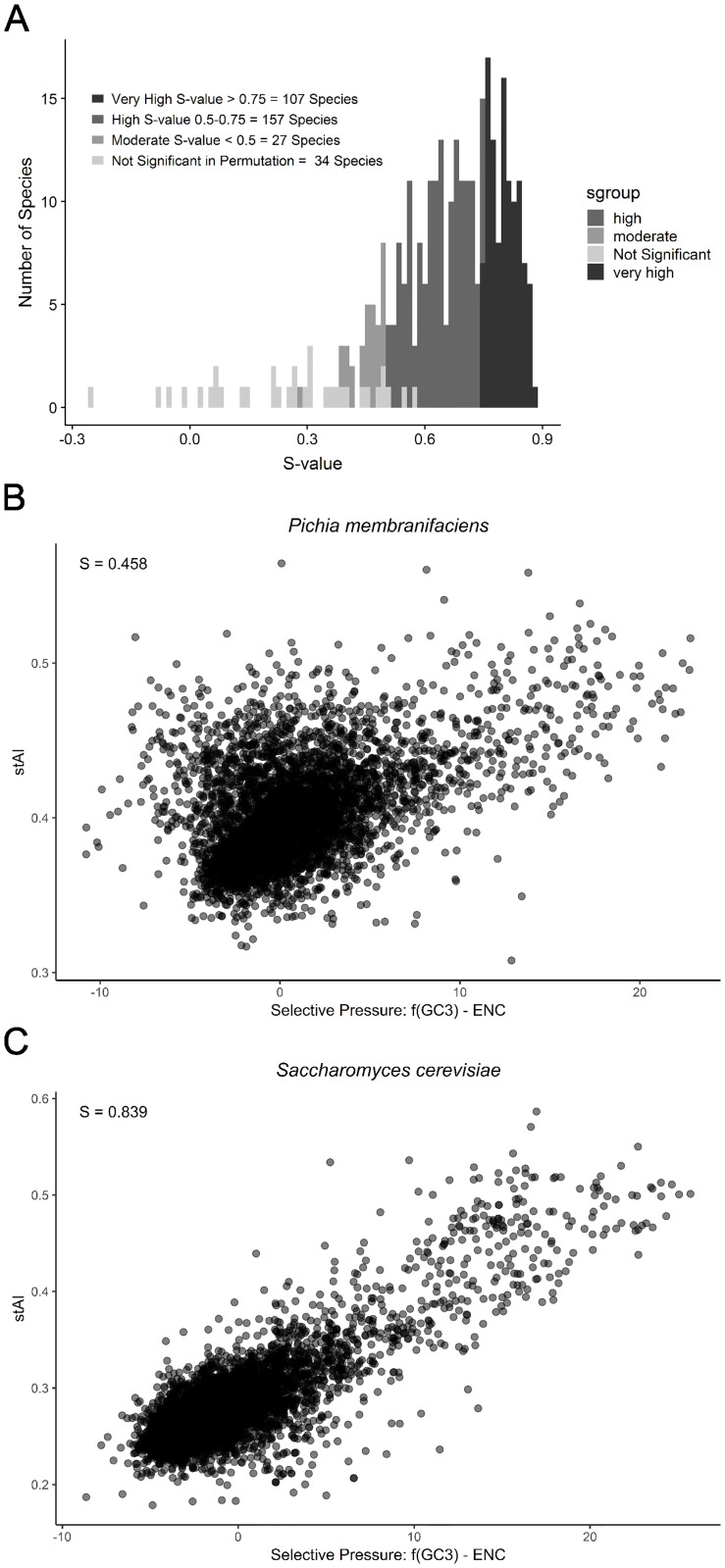
Fig 6. Most genomes in the budding yeast subphylum exhibit moderate to high levels of translational selection on codon bias.
Translational selection on codon bias was measured using the S-test, which examines the correlation between the stAI value and the selective pressure (estimated by f(GC3)-ENC where f(GC3) is a modified function of Wright’s neutral relationship between the silent GC content of a gene and the effective number of codons) on all coding sequences in a genome. Each point in the comparison between stAI and selective pressure is a single coding sequence in one genome. Higher S-values indicate higher levels of translational selection on codon bias. A) Distribution of the significant S-values (p<0.05 in permutation test; 293 species out of 327) and non-significant S-values (p>0.05 in permutation test; 34 / 327 species). B) Pichia membranifaciens, an example of a species that exhibits low translational selection on codon bias (p<0.05 in permutation test; n = 10,000). C) Saccharomyces cerevisiae, an example of a species that exhibits high translational selection on codon bias (p < 0.01 in permutation test; n = 10,000).