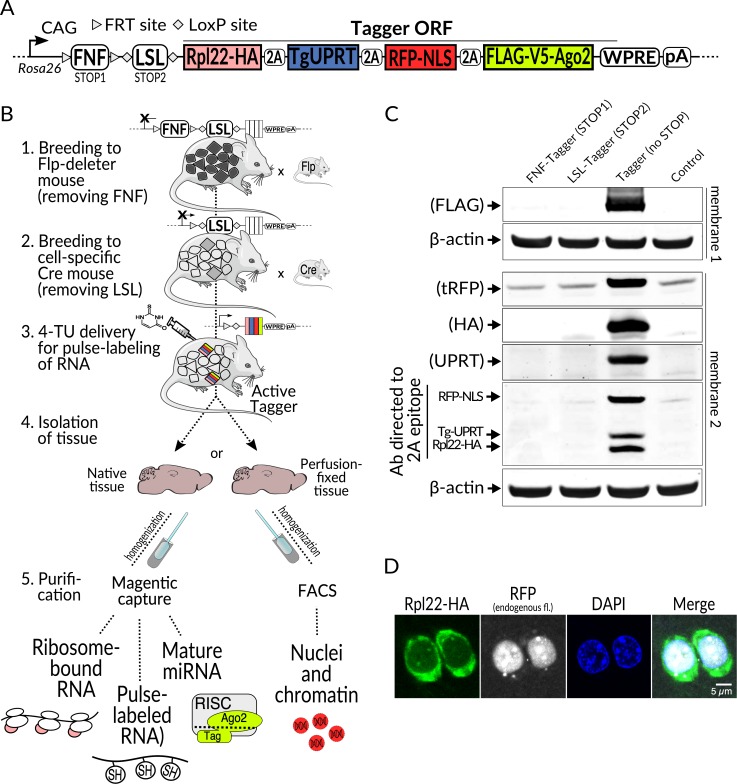
Fig 1. Overview of the Tagger system and validation of expression.
(A) Schematic of the Rosa26 knock-in Tagger transgene. From left to right: CAG—ubiquitous synthetic CAG promoter; Frt-NeoR-Frt (FNF) and LoxP-STOP-LoxP (LSL) transcriptional STOP cassettes flanked by sites for specific recombinases (Flp and Cre, respectively), allowing cell type–specific, intersectional activation of expression; single ORF encoding four proteins (in colors) separated by 2A peptides:—hemagglutinin-tagged large subunit ribosome protein 22 (Rpl22-HA, Ribo-Tag), Toxoplasma gondii Uracil phosphoribosyltransferase (TgUPRT, TU-Tag), red fluorescent protein with three NLSs (RFP-NLS, Nuc-Tag), and FLAG- and V5-tagged Argonaute2 protein (FLAG-V5-Ago2, Ago-Tag); WPRE; pA. (B) Example experimental workflow. After transgene activation by breeding to (1) Flp and (2) Cre mice, 4-Thiouracil is injected subcutaneously for metabolic RNA labeling (3); alternatively, breeding to Cre and Flp double transgenic mice would enable intersectional activation by both recombinases. Tissue is then isolated (4), homogenized, and subjected to enrichment of choice (5): affinity purification(s) or FACS of nuclei after optional perfusion-fixation. (C) Immunoblot validation of separation of all four Tagger components. Top, individual components are detected with antibodies against specific epitopes, labeled on the left. Bottom, detection with a 2A-specific antibody reveals comparable expression levels for the three components with the residual 2A epitope. Probing was done with the same samples at equal loading amounts on two different membranes. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of brain cryosection from a vGluT2-Tagger mouse showing separation of tagger components Rpl22-HA (stained with anti-HA antibody) and RFP-NLS (endogenous fluorescence). The section was counterstained with DAPI. Ago2, Argonaute 2; CAG, cytomegalovirus:chicken actin fusion promoter; Cre, causes recombination; FACS, fluorescence activated cell sorting; Flp, flippase; FNF, Frt-NeoR-Frt; Frt, flippase recognition target; LSL, LoxP-STOP-LoxP; NeoR, neomycin resistance; NLS, nuclear localization signal; ORF, open reading frame; pA, polyadenylation signal; RFP, red fluorescent protein; Rpl22-HA, hemagglutinin-tagged large subunit ribosomal protein 22; tRFP, turbo red fluorescent protein; vGluT2, vesicular glutamate transporter 2; WPRE, Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Postranscriptional Response Element.