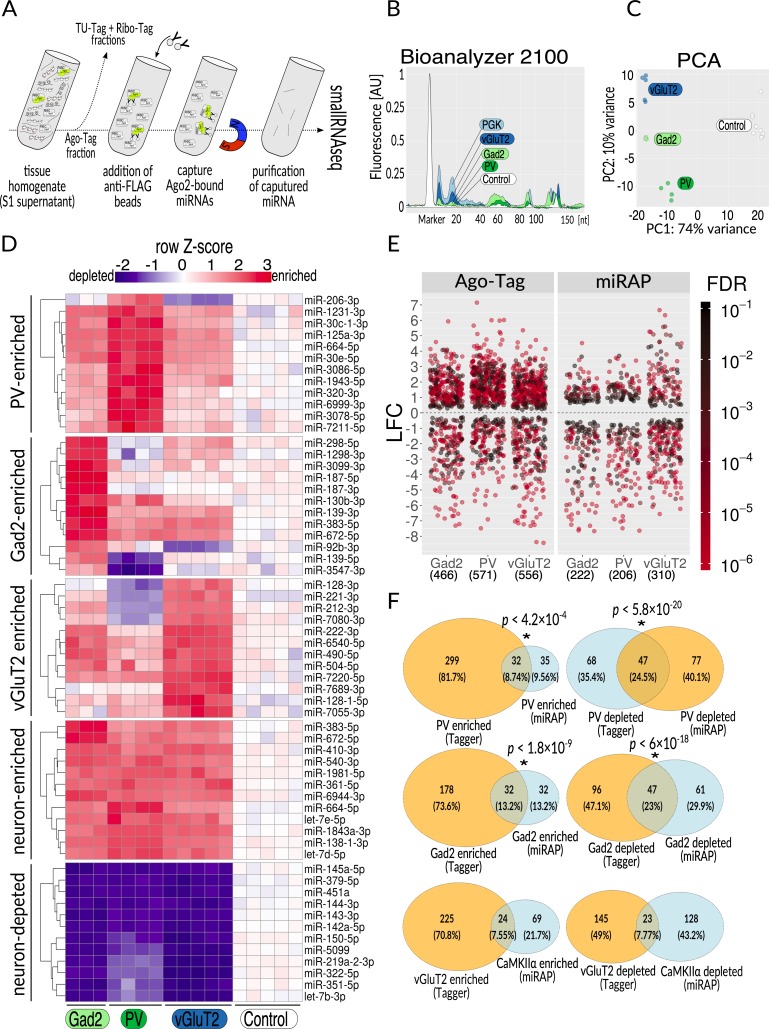
Fig 4. Ago-Tag.
(A) Overview of the procedure. Tissue homogenate, following removal of nuclei and cell debris (S1 supernatant), is split into fractions for purifying specific classes of nucleic acids. The Ago-Tag fraction is then mixed with anti-FLAG epitope magnetic beads to enrich for Ago-Tag bound to mature miRNAs. The latter are then purified and subjected to small RNAseq. (B) Agilent bioanalyzer profiles of Ago-Tag–purified miRNA. Relative amounts of RNA correspond to the proportion of the analyzed cell population in the brain (color coded), determined by the Cre line that was used (balloon labels, control = no Cre). (C) PCA of the data from three analyzed cell populations and input (S1 supernatant). (D) Heatmap showing relative distribution of VST-normalized counts (calculated using DEseq2 package) for 60 miRNAs assigned to one of five groups: PV enriched, Gad2 enriched, vGluT2 enriched, neuron enriched, and neuron depleted. miRNAs for each group were chosen on the basis of the rank metric (see Methods), by taking the top 12 genes with |LFC| > 1 and FDR < 0.1 and according to the ranking formula (left side of respective heatmap). Z-score for each row was calculated as Z = (x–mean(input))/SD(row), where SD is standard deviation. The complete set of TPM values on which panel D is based can be found in S1 Data. (E) Comparison of distribution of significantly (|LFC| > 1, FDR < 0.1) changed miRNAs in Ago-Tag and miRAP [11]; numbers in parentheses denote the number of changed miRNAs. (F) Overlap of significantly enriched (LFC > 1, FDR < 0.1) and significantly depleted (LFC > 1, FDR < 0.1) miRNAs between Ago-Tag data and miRAP [11] data. Asterisks denote statistically significant overlaps (hypergeometric test, see also S3 Table). Note the lack of statistical significance for comparisons of data obtained with different Cre drivers (vGluT2-Cre versus CaMKIIα-Cre). Ago2, Argonaute 2; AU, arbitrary unit; CaMKIIα, calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II; Cre, causes recombination; FDR, false discovery rate; Gad2, glutamic acid decarboxylase 2; LFC, Log2 fold change; miRAP, miRNA affinity purification; miRNA, microRNA; PCA, principal component analysis; PV, parvalbumin; RNAseq, RNA sequencing; TPM, transcripts per million; vGluT2, vesicular glutamate transporter 2; VST, variance stabilizing transformation.