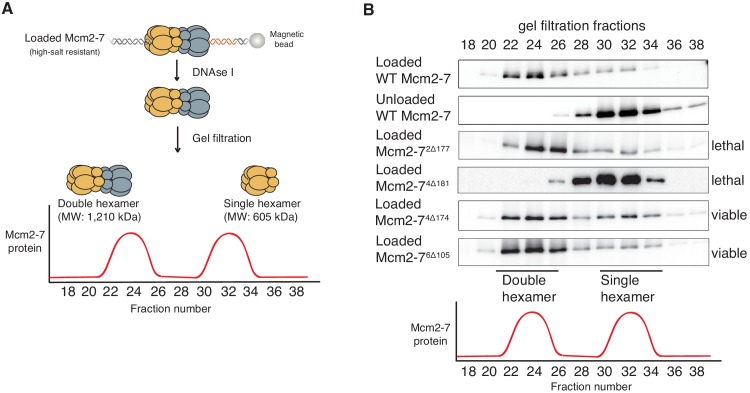
Figure 2. Deletion of the Mcm4 N-terminal region inhibits Mcm2-7 double-hexamer formation.
(A) Double-hexamer assay scheme. After performing a helicase-loading reaction with purified proteins and high-salt wash, loaded Mcm2-7 complexes were released from the bead-bound DNA by DNase I treatment. Released Mcm2–7 complexes were fractionated by gel filtration to separate double from single hexamers. (B) Mcm2-74Δ181 is defective for double-hexamer formation. Mcm2-7 complexes including the indicated N-terminal deletions were tested for their ability to form double hexamers as described in (A). The Flag-Mcm3 subunit of the Mcm2-7 complexes in the indicated fractions was detected by immunoblot. Wild-type Mcm2-7 double hexamers eluted early (fraction 22–26), whereas purified Mcm2-7 eluted later (fraction 30–34). Mutant viability data (right) are from Figure 1C.