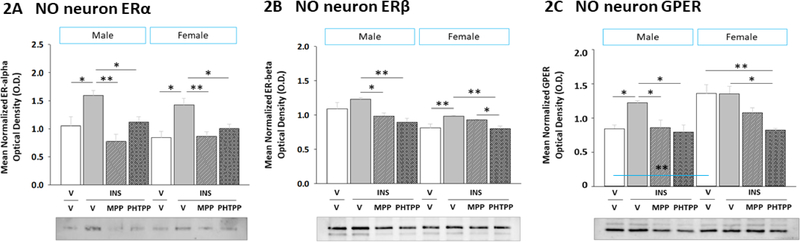
Figure 2. Effects of Intracerebroventricular (icv) Administration of the ERα Antagonist 1,3-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-methyl-5-[4-(2-piperidinylethoxy)phenol]-1H-pyrazole dihydrochloride (MPP) or the ERβ Antagonist 4-[2-phenyl-5,7-bis(trifluoromethyl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]phenol (PHTPP) on VMN Nitrergic Neuron Estrogen Receptor-Alpha (ERα), Estrogen Receptor-Beta (ERβ), and G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor (GPER) Protein Expression in Insulin-Induced Hypoglycemic (IIH) Male versus Female Rats.
Pooled lysates of laser-catapult microdissected VMN nNOS-immunoreactive (-ir) neurons created for each treatment group were evaluated by Western blot for ERα [Panel A; male data at left, female data at right], ERβ [Panel B; male data at left, female data at right], and GPER [Panel C; male data at left, female data at right] protein expression in groups of vehicle-pretreated male or female rats injected subcutaneously (sc) with either vehicle (solid white bars; n=6 males, n=6 females) or neutral protamine Hagedorn insulin (INS; 10.0 U/kg bw; solid gray bars; n=6 males, n=6 females) and groups of INS-injected animals of either sex that were pretreated with MPP (diagonal-striped gray bars; n=6 males, n=6 females) or PHTPP (cross-hatched gray bars; n=6 males, n=6 females). Data depict mean normalized protein O.D. ± S.E.M. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA for sex versus treatment. *p <0.05; **p <0.01; ***p <0.001.